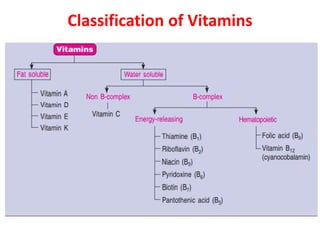
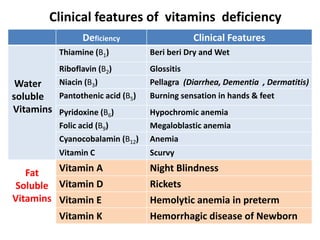
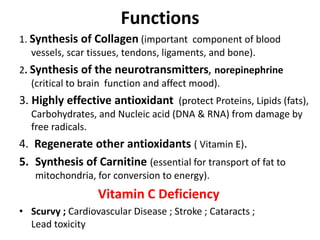
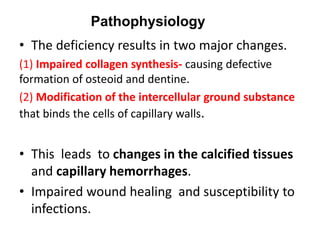
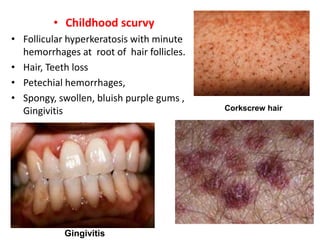
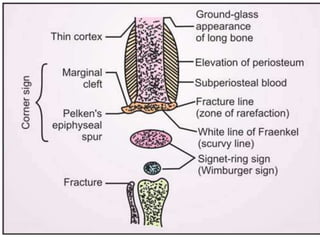
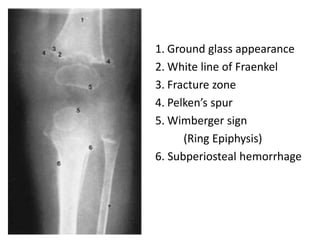
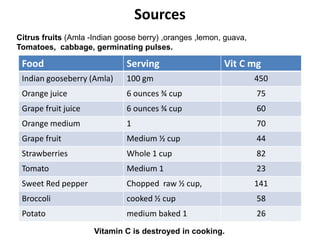
This document summarizes scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. It discusses that vitamin C is required in the diet and its functions include collagen synthesis and acting as an antioxidant. Scurvy's clinical features include bleeding gums, joint pain, and weakness. In infants, signs include irritability and pseudoparalysis. Diagnosis is usually clinical but may include low vitamin C blood levels. Treatment involves vitamin C supplementation with a loading dose followed by daily doses. Prevention recommendations include breastfeeding, vitamin C supplementation in artificial feeding, and including citrus fruits and other vitamin C sources in the diet.