Pathophysiology and clinical management of gouty arthritis
- 2. CONTENT: • Definition • Epidemiology • Etiology • Pathophysiology • Classification of gout • Risk factors • Stages of gout • Signs and symptoms • Diagnosis • Treatment • Lifestyle modifications
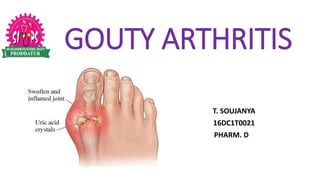
- 3. DEFINITION: Gout is the most common inflammatory and metabolic joint disorder which is caused by the deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints and soft tissues following chronic hyperuricaemia. chronic hyperuricaemia is associated with disorders of purine metabolism due to underexcretion or overproduction of uric acid, the final metabolite of endogenous and dietary purine metabolism.
- 4. EPIDEMIOLOGY: Gout is one of the oldest recognised disease and was identified by the Egyptians in 2460 B.C. Gout affects 1-2% of adults in developed countries and in recent decades there has been a great significant rise in its prevalence and incidence. The USA has seen a doubling in the number of cases with a rate of gout increasing to 4.1% in older males. Gout is predominantly a disease of men with a male to female ratio of 36:1. In women, it tends to develop after menopause when levels of oestrogen, a known uricosuric fall.
- 5. ETIOLOGY: Although environmental factors are clearly implicated in the development of gout, inheritance also play an important role. In recent years, research into genetic background of gout has identified several renal urate transporters including URAT-1 & GLUT-9 and the genes encoding for them. E.g. SLC22A12 & SLC2A9 respectively. Polymorphism in these genes are associated with increased hyperuricaemia and gout.
- 6. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: In humans, uric acid is the end product of the degradation of purines. Uric acid has no known physiologic purpose and therefore is regarded as a waste product. In lower animals, the enzyme uricase breaks down uric acid to the more soluble allantoin, and thus uric acid does not accumulate. Gout occurs exclusively in humans in whom a miscible pool of uric acid exists. Under normal conditions, the amount of uric acid is about 1200mg in men & about 600mg in women. The size of the urate pool is increased several fold in individuals with gout. This excess accumulation may result from either overproduction or underexcretion.
- 7. Contd... The purines from which uric acid is produced originate from three sources: 1. Dietary purine 2. Conversion of tissue nucleic acid to purine nucleotides 3. de novo synthesis of purine bases The purines derived from these three sources enter a common metabolic pathway leading to the production of either nucleic acid or uric acid. Under normal circumstances, uric acid may accumulate excessively if production exceeds excretion.
- 8. Contd... Several enzyme systems regulate purine metabolism. Abnormalities in these regulatory systems can result in overproduction of uric acid. Two enzyme abnormalities resulting in an overproduction of uric acid are: 1. Increase in the activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) synthetase, which leads to increased concentration of PRPP. PRPP is a key determinant of purine synthesis and thus uric acid production. 2. Deficiency of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT), which is responsible for the conversion of guanine to guanylic acid & hypoxanthine to inosinic acid.
- 9. Contd... These two conversions require PRPP as the co-substrate and are important reutilization reactions involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A deficiency in the HGPRT enzyme leads to increased metabolism of guanine and hypoxanthine to uric acid and more PRPP to interact with glutamate in the first step of purine pathway. Complete absence of HGPRT results in the childhood Lesch-nyhan syndrome, characterised by choreoathetosis, spasticity, mental retardation and markedly excessive production of uric acid. A partial deficiency of the enzyme may be responsible for marked hyperuricaemia in otherwise normal, healthy individuals.
- 11. CLASSIFICATION OF GOUT: Gout can be classified as primary or secondary, depending upon the presence or absence of an identified cause of hyperuricaemia. 1. Primary gout: Here the basic metabolic defect is unknown. Elevated serum uric acid levels may be due to following: a) Increased production of uric acid due to excessive dietary purines or due to rare enzyme mutation defects (Lesch-Nyhan syndrome due to deficiency of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl tranferase (HGPRT); variants in enzyme phosphoribosyl- 1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) have increased de novo purine production). b) Undersecretion of uric acid results from a defect in renal excretion.
- 12. Contd... 2. Secondary gout: It is associated with increased nucleic acid turnover, decreased renal function, increased purine production or drug induced (diuretics, aspirin less than 2g/day, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, nicotinic acid, ethanol, cyclosporine, methoxyflurane, levodopa and epinephrine), deficiency of glucose- 6 –phosphatase, myeloid proliferative disorders, psoriasis, exercise and uncontrolled diabetes.
- 13. RISK FACTORS: Hyperuricaemia is one of the main risk factors for gout and occurs in about 15-20% of the population. Fortunately, only a minority of individuals with increased serum uric acid levels develop gout suggesting the importance of other contributing factors: 1. Genetics 2. Renal disease 3. Diet 4. Alcohol consumption 5. Co-morbidities e.g. Obesity, dyslipidaemia, glucose intolerance, hypertension 6. Medication
- 14. STAGES OF GOUT:
- 15. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: • Fever • Intense pain • Erythema • Warmth and swelling of involved joints. • Excruciating pain, swelling and inflammation involving one or more joints, most commonly starting in the great toe, but sometimes involving other joints of the extremities.
- 16. DIAGNOSIS: Tests that help to diagnose gout may include: • Joint fluid test: A needle is inserted to draw a fluid from the affected joint. Urate crystals may be visible when the fluid is examined under a microscope. • Blood test: Blood test is recommended to measure the levels of uric acid and creatinine in blood. Blood test results can be misleading, though. Some people have high uric acid levels, but never experience gout and some people have signs & symptoms of gout, but don’t have unusual levels of uric acid in their blood.
- 17. Contd... • X-ray imaging: Joint X-rays cam be helpful to rule out other causes of joint inflammation. • Ultrasound: Musculoskeletal ultrasound can detect urate crystals in a joint or in a tophus. This technique is more widely used in Europe than in the United States. • Dual energy CT scan: This type of imaging can detect the presence of urate crystals in a joint, even when it is not acutely inflamed. This test is not used routinely in clinical practice due to the expense and is not widely available.
- 18. TREATMENT: Treatment aims in gout: • Rapid alleviation of the acute attack. • Prevention of future attacks. • Lower serum uric acid levels to below saturation point. • Reduce risk of co-morbidities. E.g. Cardiovascular disease. • Lifestyle modification.
- 19. MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE GOUT: Drugs used in the management of an acute attack include: 1. First line: NSAIDs (use maximum dose) 2. Second line: Colchicine 3. Third line: Corticosteroids like prednisolone, methylprednisolone, triamcinolone
- 20. 1. NSAIDs: MOA: NSAIDs (Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) act by direct inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) via blockade of the cyclooxygenase enzyme site. The subsequent inhibition of prostaglandin production reduces inflammation, but also results in additional activities on platelet aggregation, renal homeostasis and mucosal injury. ADRs: Upper GI effects, acute tubular necrosis, hepatotoxicity, vasculitis etc. Dose: Indomethacin-25mg TID, Diclofenac-25-50mg TID.
- 21. 2. COLCHICINE: MOA: It is an alkaloid used to relieve acute attack of gouty arthritis. It is not an analgesic and uricosuric agent, although it relieves pain in acute attack. Colchicine inhibits migration of neutrophils to the affected area. ADRs: Andominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and rarely bone marrow supression, neuropathy and myopathy. Dose: Tablets-0.5, 0.6mg (0.5-1.2mg PO followed by 0.5-1.2mg every 1- 2hrs). Injection-1mg/2ml (1mg initially, followed by 500mcg every 2- 3hrs).
- 22. 3. CORTICOSTEROIDS: MOA: Corticosteroids act by inhibiting cytokine release and give rapid relief of symptoms and decrease inflammation. They can be given oral, intravenous or intraarticular routes. ADRs: Diabetes, increased risk of infection, hypertension, weight gain, insomnia, menstrual irregulations, osteoporosis, psychosis etc. Dose: Methyl prednisolone-80mg or 40mg, Triamcinolone-40mg, Oral prednisolone-30mg.
- 23. Algorithm for managing acute gout
- 24. MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC GOUT: Some patients may only experience a single episode and a change in lifestyle, diet or concurrent medication may be sufficient to prevent further attacks. Patients who suffer one or more acute attacks within 12 months of the first attack should normally be prescribed prophylactic urate-lowering therapy. Classification of prophylactic agents used to lower serum urate: 1. Uricostatic agents: allopurinol, febxostat 2. Uricosuric agents: Benzbromarone, probenecid, sulphinpyrazone 3. Uricolytic agents: rasburicase, polyethylene glycol-uricase
- 25. Contd... The criteria for starting prophylactic treatment for gout: 1. One or more acute attacks within 12 months of the first attack. 2. Tophi present at the first presentation of an acute attack. 3. Presence of uric acid stones. 4. Need to continue medication associated with raised uric acid levels. e.g. Diuretics. 5. Young patients with a family history of renal or cardiac disease.
- 26. 1. URICOSTATIC AGENTS: MOA: They inhibit the enzyme xanthine oxidase, which is essential for the conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine and then to uric acid. Thereby they prevent the synthesis of uric acid and the plasma concentration of uric acid is reduced. ADRs: Rashes, itching, erythema, GI disturbances like nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, hepatotoxicity, fever, headache. Dose: Allopurinol-100mg/day Febuxostat-80mg or 120mg/day
- 27. 2. URICOSURIC AGENTS: MOA: They inhibit active tubular reabsorption of uric acid in proximal tubules and thereby increase excretion of uric acid. ADRs: GI disturbances like nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, ulceration, blood disorders. Dose: Benzobromarone-50-200mg/day Probenecid-0.5-2gm/day Sulphinpyrazone-200-800mg/day
- 28. 3. URICOLYTIC AGENTS: MOA: They convert the uric acid to more soluble allantoin and increase its excretion through urine. ADRs: Haemolysis, GI disturbances, hypersensitivity reactions like skin rashes may occur. Dose: Rasburicase-0.2mg/day for 5-7days Poly ethylene glycol-uricase-3.5gm/day
- 29. Algorithm for managing chronic gout
- 30. LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS: Medications are often most effective way to treat acute gout and can prevent recurrent attacks of gout. However, making certain lifestyle changes also are important, such as: 1. Limiting alcoholic beverages & drinks sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose). Instead, drink plenty of non-alcoholic beverages, especially water. 2. Limiting intake of foods high in purines such as red meat, organ meats and seafood. 3. Exercising regularly and losing weight. Keeping body at a healthy weight reduces the risk of gout.
- 31. REFERENCES/BIBLIOGRAPHY: • Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics- Roger & Walker, Churchill Livingstine publication-5th edition. • Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiological approach by Joseph T. Dipiro. • Elements of clinical pharmacy by Dr. Ramesh K.Goyal, Dr. Parloop A. Bhatt, Dr. Mahesh D. Burande.
