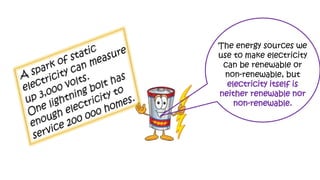
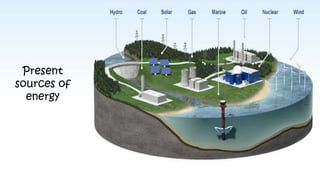
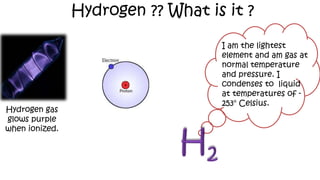
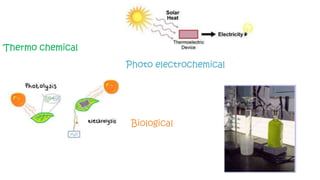
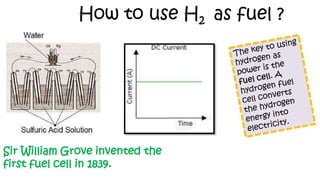
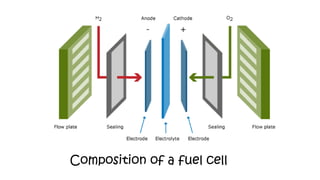
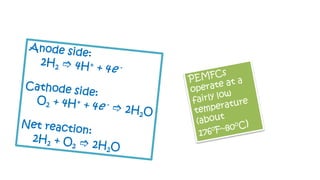
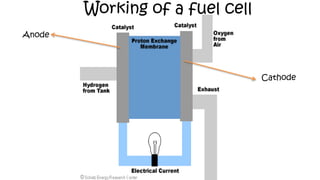
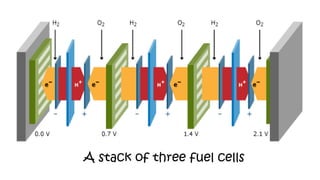
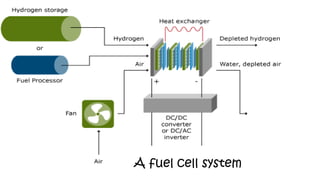
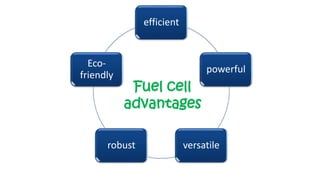
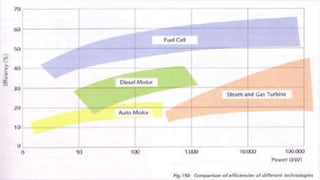
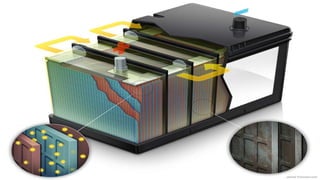
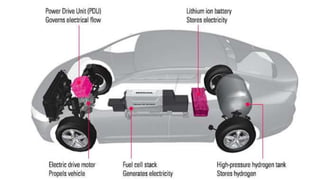
The document discusses hydrogen fuel cells and electricity, highlighting that electricity is an energy carrier derived from various sources. It explains hydrogen's properties as the lightest element and its role in energy storage and transport, akin to a battery. Additionally, the document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of fuel cells, including efficiency comparisons and safety concerns related to hydrogen gas.