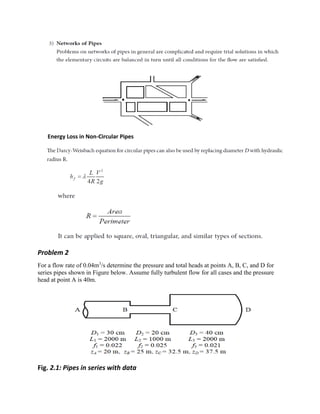
The document discusses hydraulic principles for analyzing flow through pipes in series and parallel configurations. It provides examples of calculating head loss, equivalent pipe coefficients, and determining flow rates and heads at different points in pipe systems. Sample problems are worked through step-by-step showing computations for pressure and total heads at nodes, equivalent roughness coefficients, head loss, and flow distribution between parallel pipes.