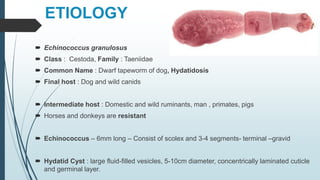
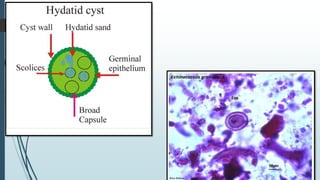
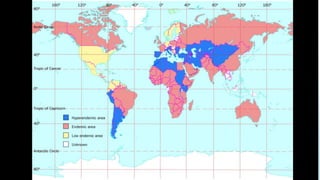
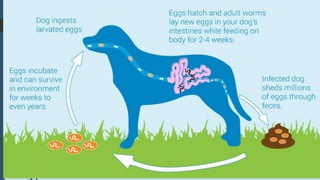
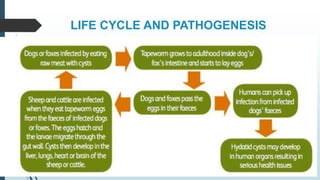
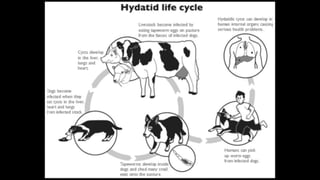
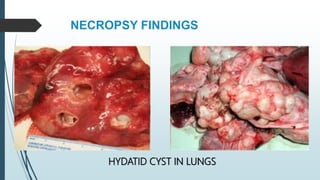
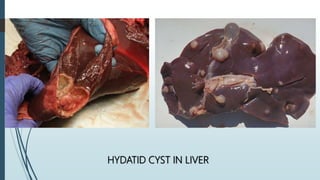
The document discusses the etiology and epidemiology of Echinococcus granulosus, a cestode responsible for hydatidosis, with dogs as final hosts and various ruminants, humans, and primates as intermediate hosts. It highlights the clinical findings, diagnosis methods, and the lack of symptoms in infected ruminants, while noting potential respiratory distress in humans. Control measures include treating dogs, restricting access to abattoirs, and the development of a recombinant vaccine requiring further refinement.