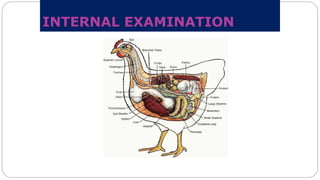
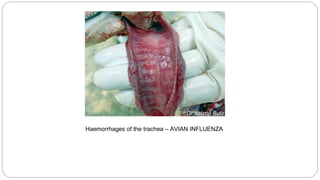
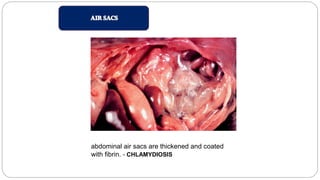
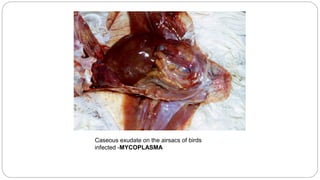
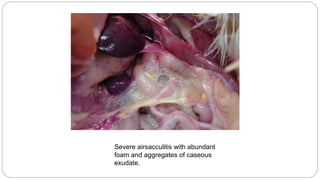
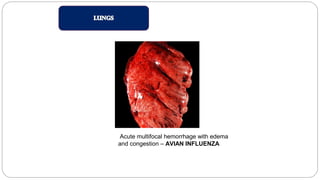
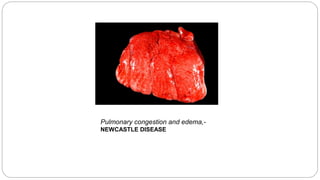
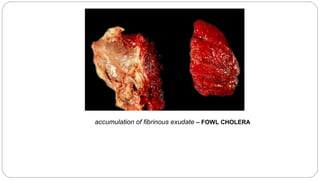
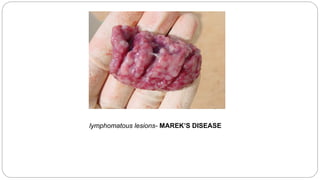
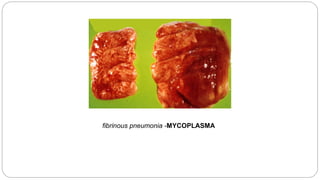
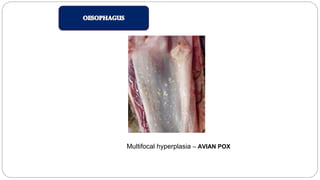
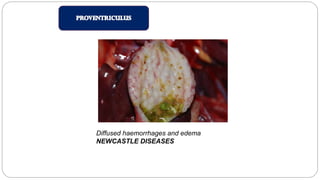
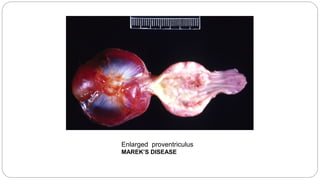
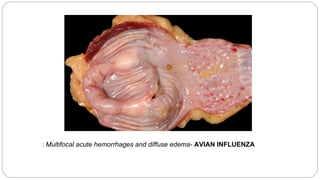
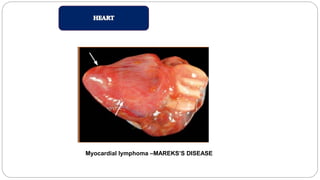
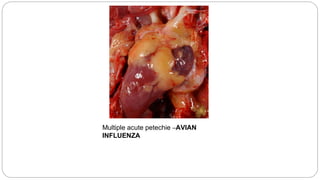
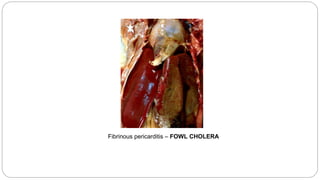
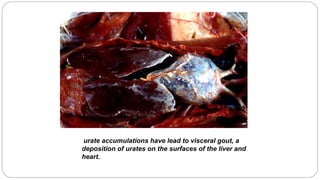
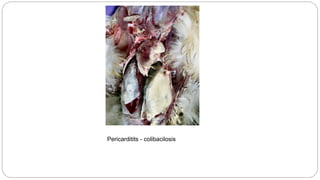
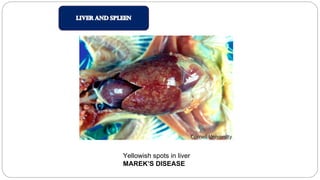
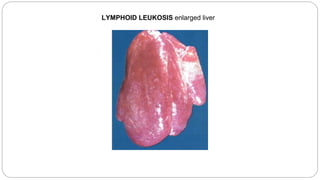
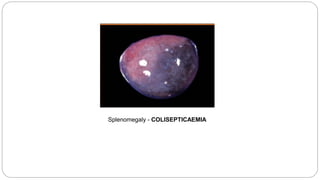
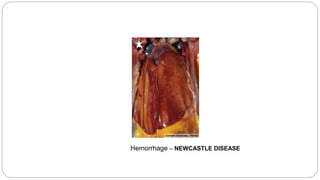
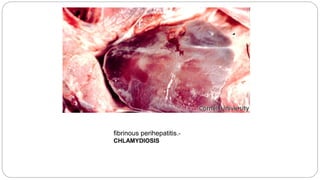
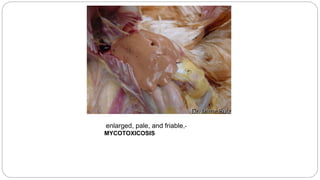
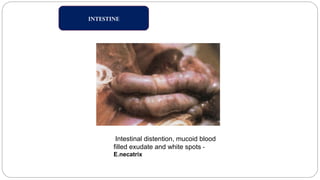
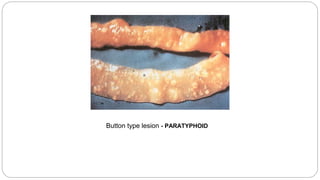
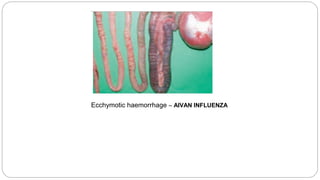
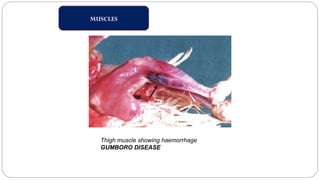
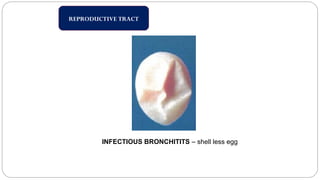
A postmortem examination of birds provides important information about the cause of death and diseases affecting the flock. The examination procedure involves obtaining a flock history, external examination of the bird for abnormalities, and internal examination of the organs. During internal examination, lesions in various organs can provide clues to diagnose diseases like avian influenza, fowl pox, Marek's disease, and others. A thorough postmortem is important for better disease diagnosis, flock management, and reducing morbidity and mortality.