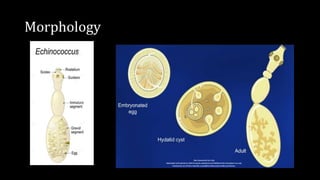
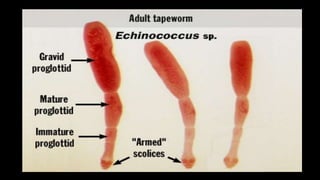
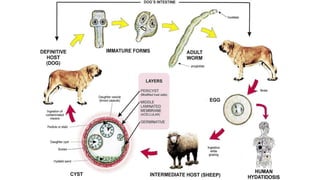
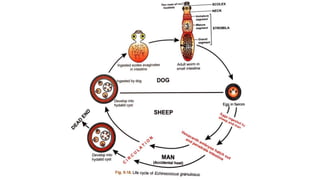
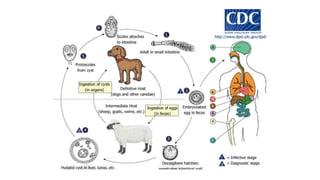
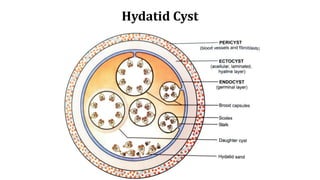
Echinococcus granulosus, commonly known as the dog tapeworm, has a two-host lifecycle between dogs and intermediate hosts such as sheep. In humans, the larval form causes hydatid cysts, most often in the liver and lungs. The cysts are fluid-filled bladders that can cause pressure effects and rupture. Diagnosis involves tests like Casoni's test, imaging, and cyst fluid examination. Treatment is usually surgical removal of cysts along with albendazole to prevent spreading, while prophylaxis focuses on hygiene and restricting dog access to slaughtered animals.