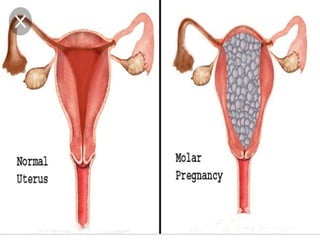
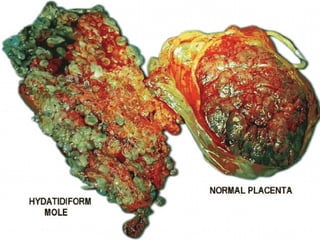
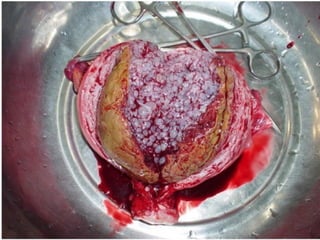
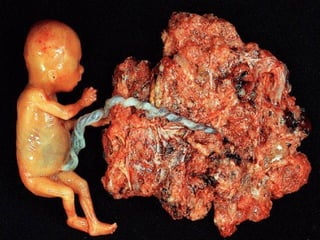
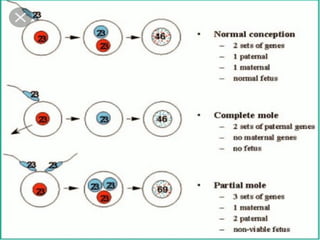
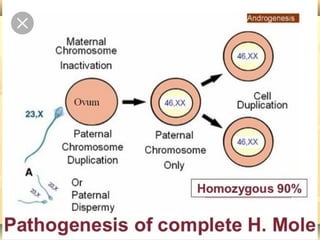
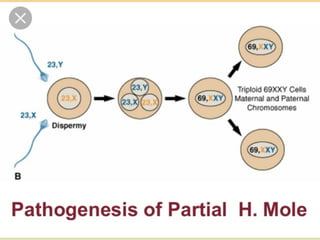
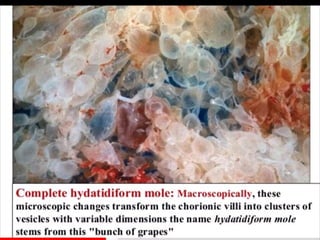
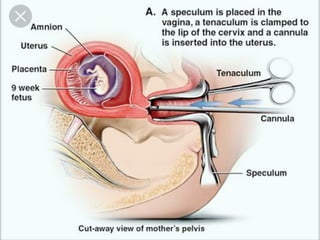
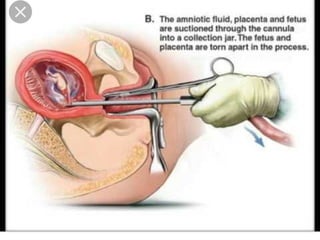
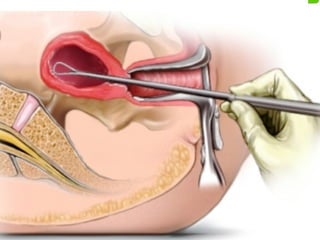
This document discusses hydatidiform mole, a rare abnormal pregnancy where the placenta develops abnormally. There are two types - complete and partial mole. Complete mole occurs when the placenta grows abnormally but there is no fetus. Partial mole occurs when both abnormal and normal placental tissue develops along with a non-viable fetus. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding, nausea, vomiting and rapid uterine growth. Diagnosis involves ultrasound, blood tests and tissue examination. Treatment is usually surgical evacuation of the uterus. Follow up is needed to monitor for complications like hemorrhage and ensure no remaining molar tissue.