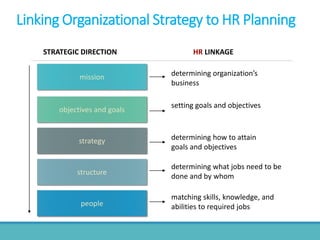
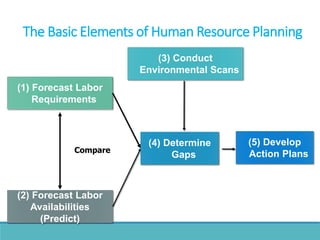
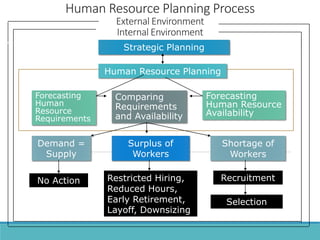
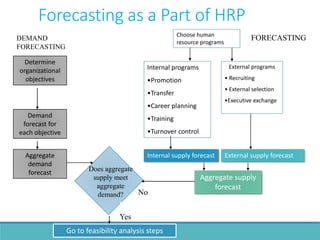
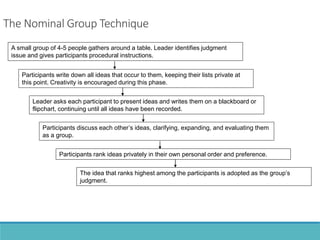
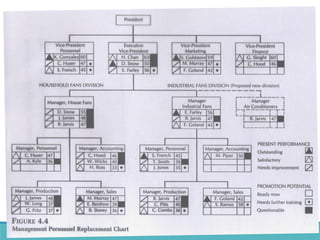
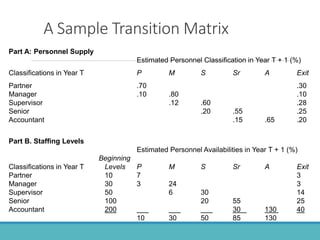
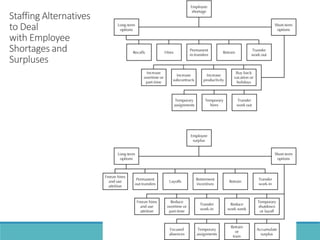
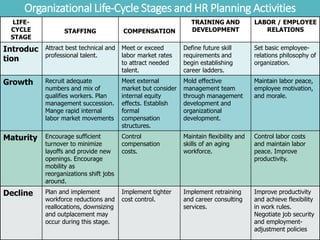
The document outlines the process and importance of human resource planning (HRP) in organizations, emphasizing the need for proper forecasting of labor demand and supply to align workforce capabilities with strategic objectives. It covers various methodologies for forecasting, the formulation of action plans, and the evaluation of HRP effectiveness, as well as strategies for addressing labor shortages and surpluses. Additionally, it addresses the challenges and limitations of HRP, including the necessity for effective data management and the need for top management support.