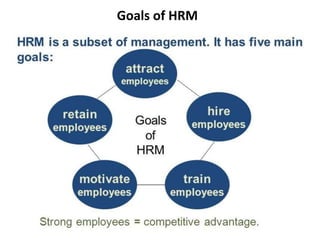
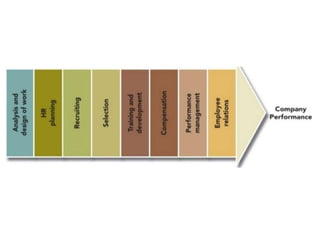
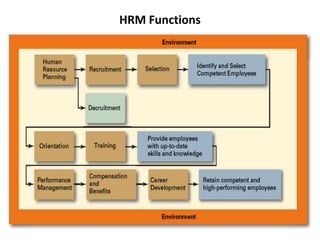
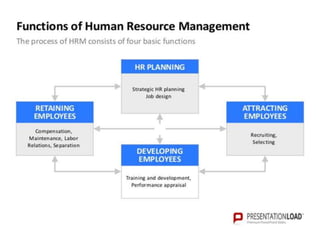
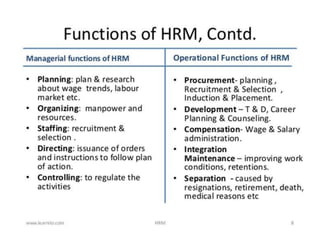
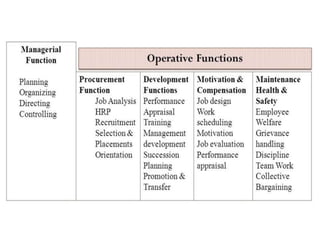
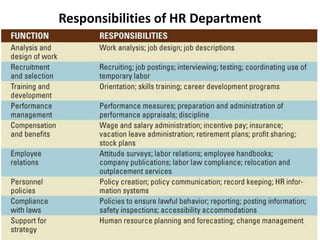
This document provides an introduction to foundations of human resource management (HRM). It defines key terms like human, resource, and management. It explains that people are the most important asset of an organization and that HRM aims to match organizational needs to employee skills and abilities. The document also outlines goals, importance, and examples of high-performance work practices of HRM. It describes common HRM functions like job analysis, human resource planning, recruiting, selection, training, compensation, performance management, and retention.