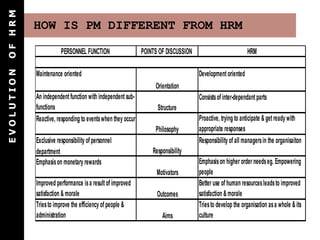
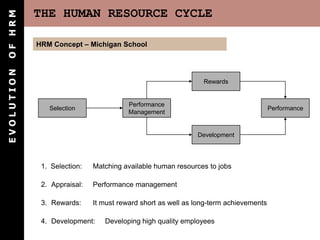
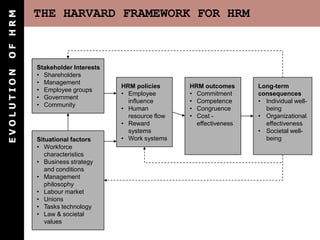
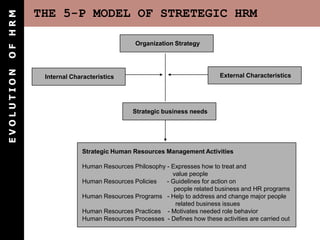
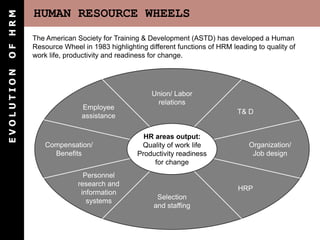
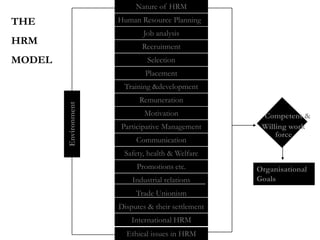
The document outlines the evolution of Human Resource Management (HRM), highlighting its transition from a maintenance-oriented personnel management to a strategic approach focused on people as valuable assets. It emphasizes the importance of integrating HRM functions such as staffing, development, appraisal, and compensation to enhance organizational effectiveness and employee satisfaction. Additionally, it covers various HRM frameworks and models that address organizational needs and advocate for continuous adaptation to changing business environments.