This document provides an overview of a human reproduction lab for an online biology course. The lab includes:
1) Watching a video on human reproduction and answering worksheet questions.
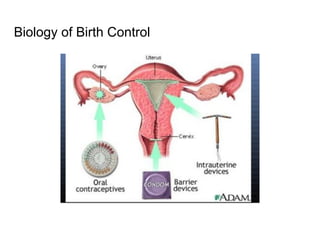
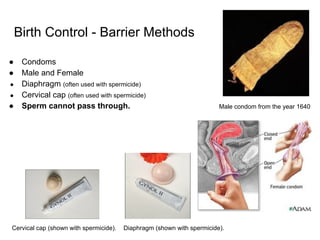
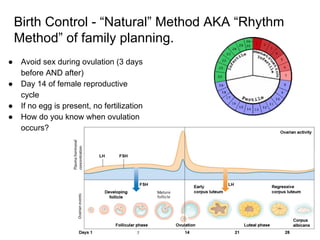
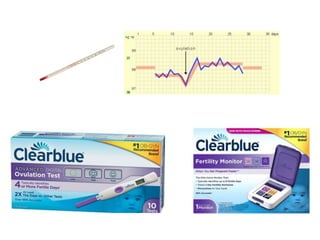
2) Reading about various birth control methods and categorizing them on a worksheet.
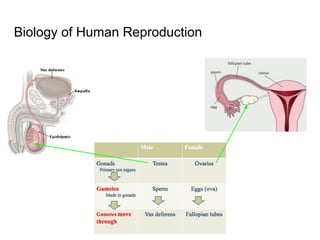
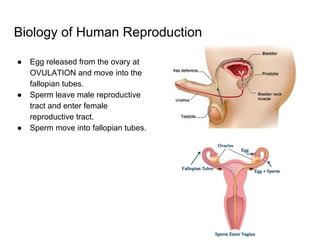
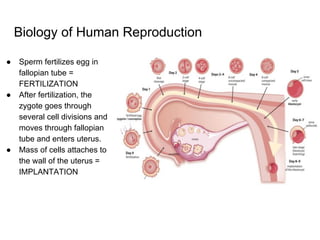
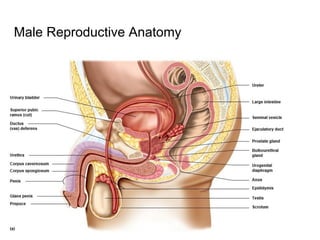
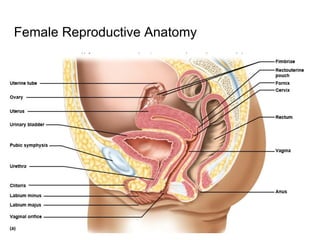
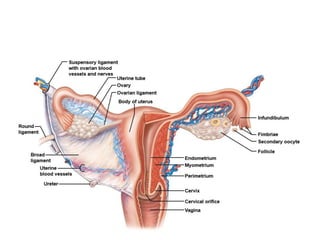
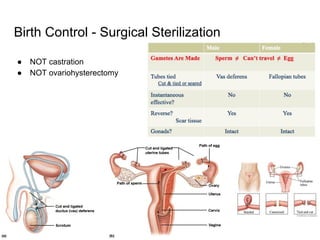
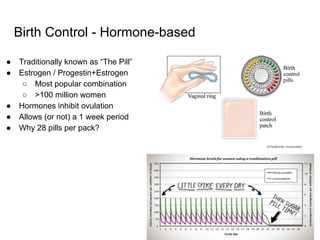
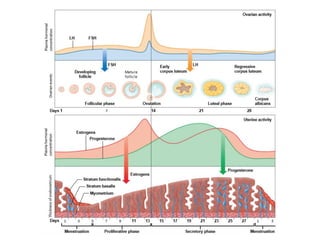
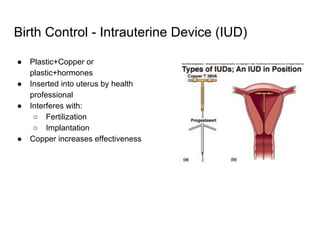
3) Taking a post-lab quiz to assess understanding of human reproductive anatomy, the biology of reproduction, and different birth control options. Diagrams and details are presented on male and female anatomy, the fertilization process, and features of common contraceptive methods like hormones, IUDs, barriers, and natural family planning.