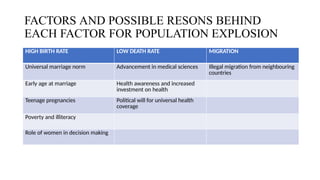
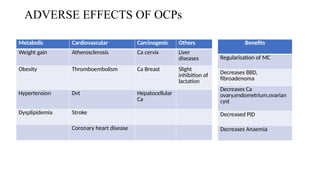
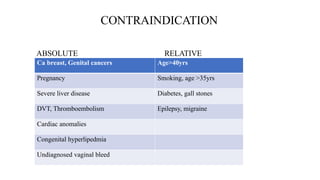
This document discusses methods of population control and family planning, including demographic processes and the importance of family size management. It details various contraceptive methods, both temporary and permanent, and their mechanisms, benefits, and contraindications. Additionally, the document emphasizes social welfare measures and initiatives necessary to effectively manage population growth.