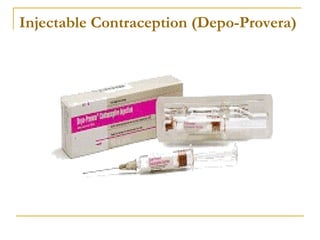
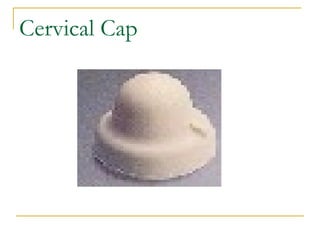
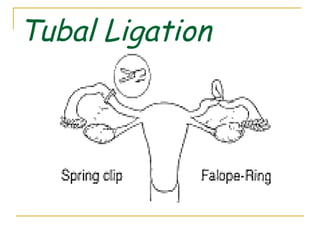
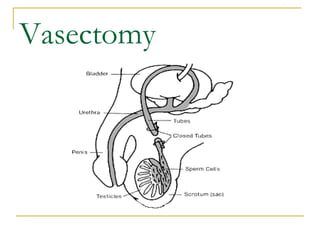
This document discusses various methods of family planning, including natural and artificial methods. Natural family planning relies on abstinence during fertile periods and includes tracking basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and menstrual cycles. Artificial methods use contraceptives to prevent pregnancy, such as condoms, diaphragms, birth control pills, IUDs, injectables, sterilization procedures like vasectomy and tubal ligation, and spermicides.