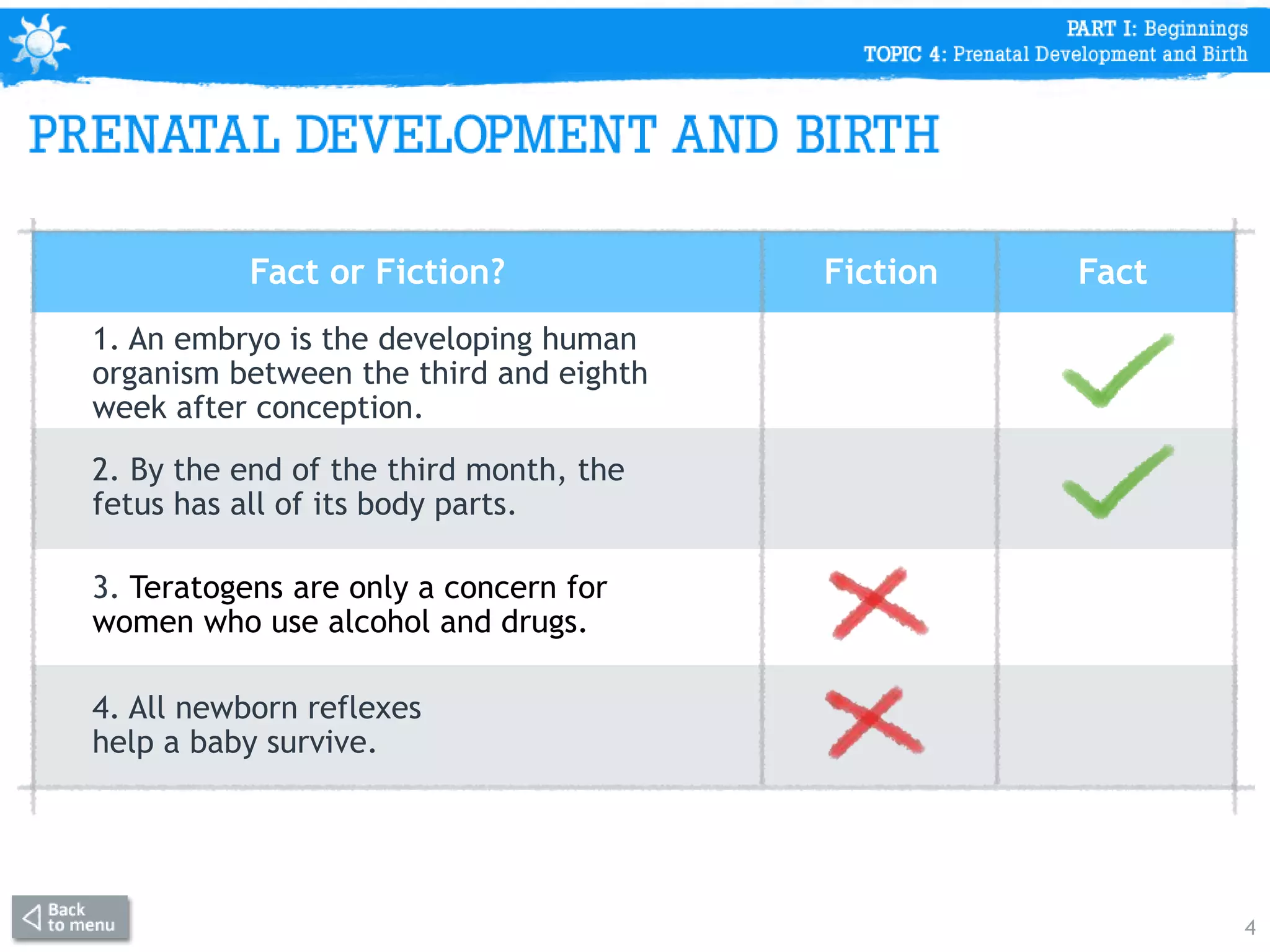
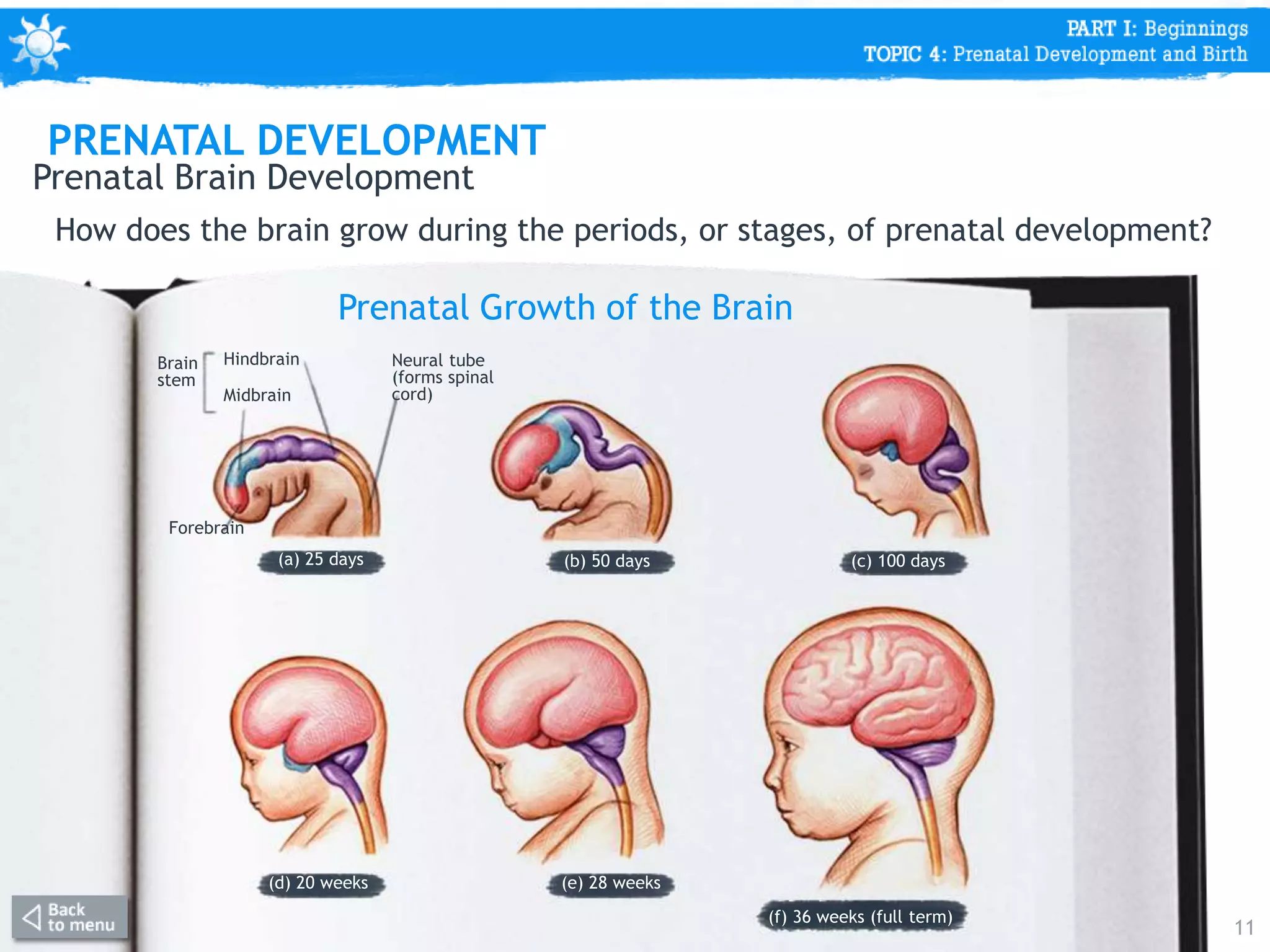
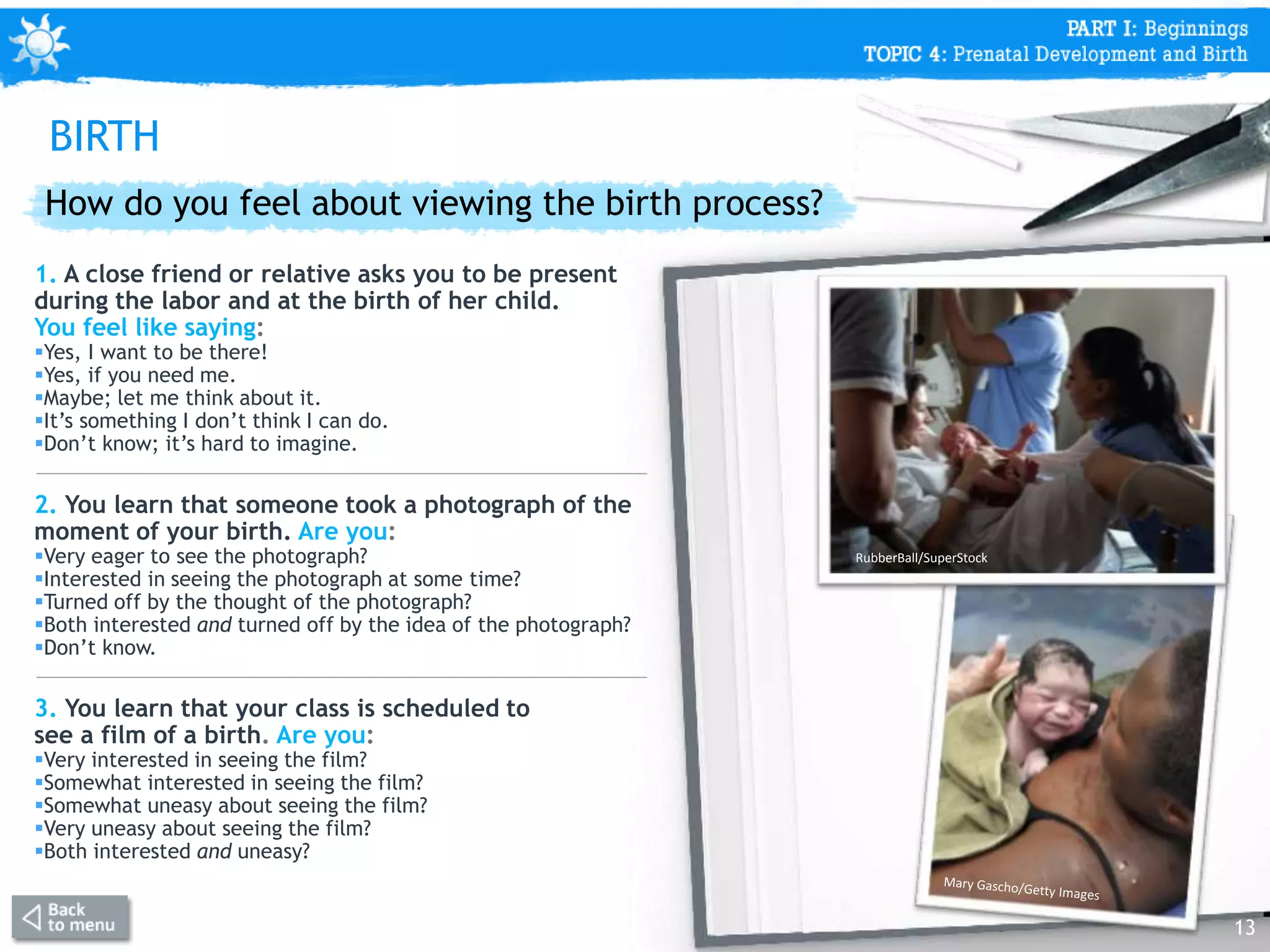
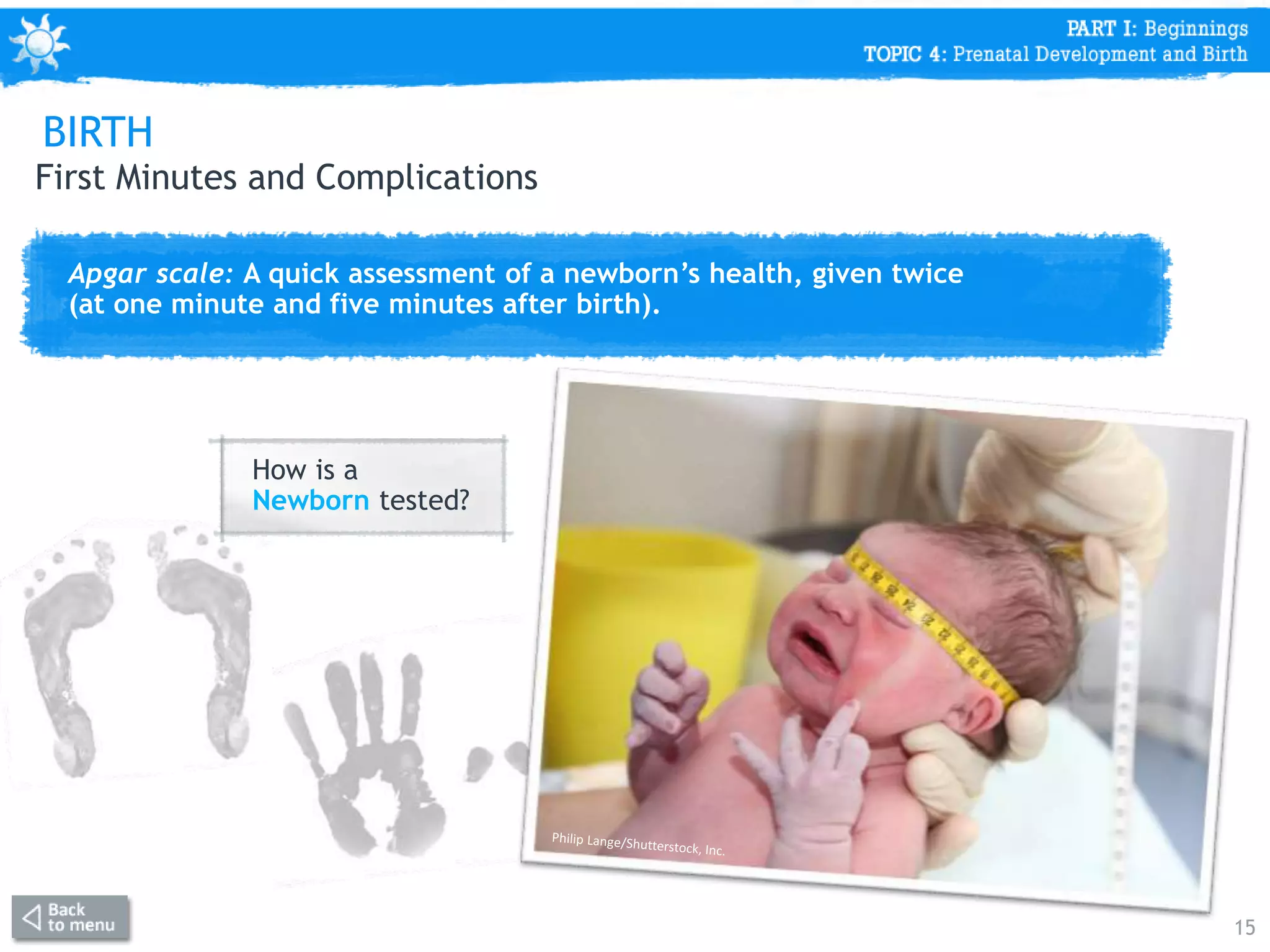
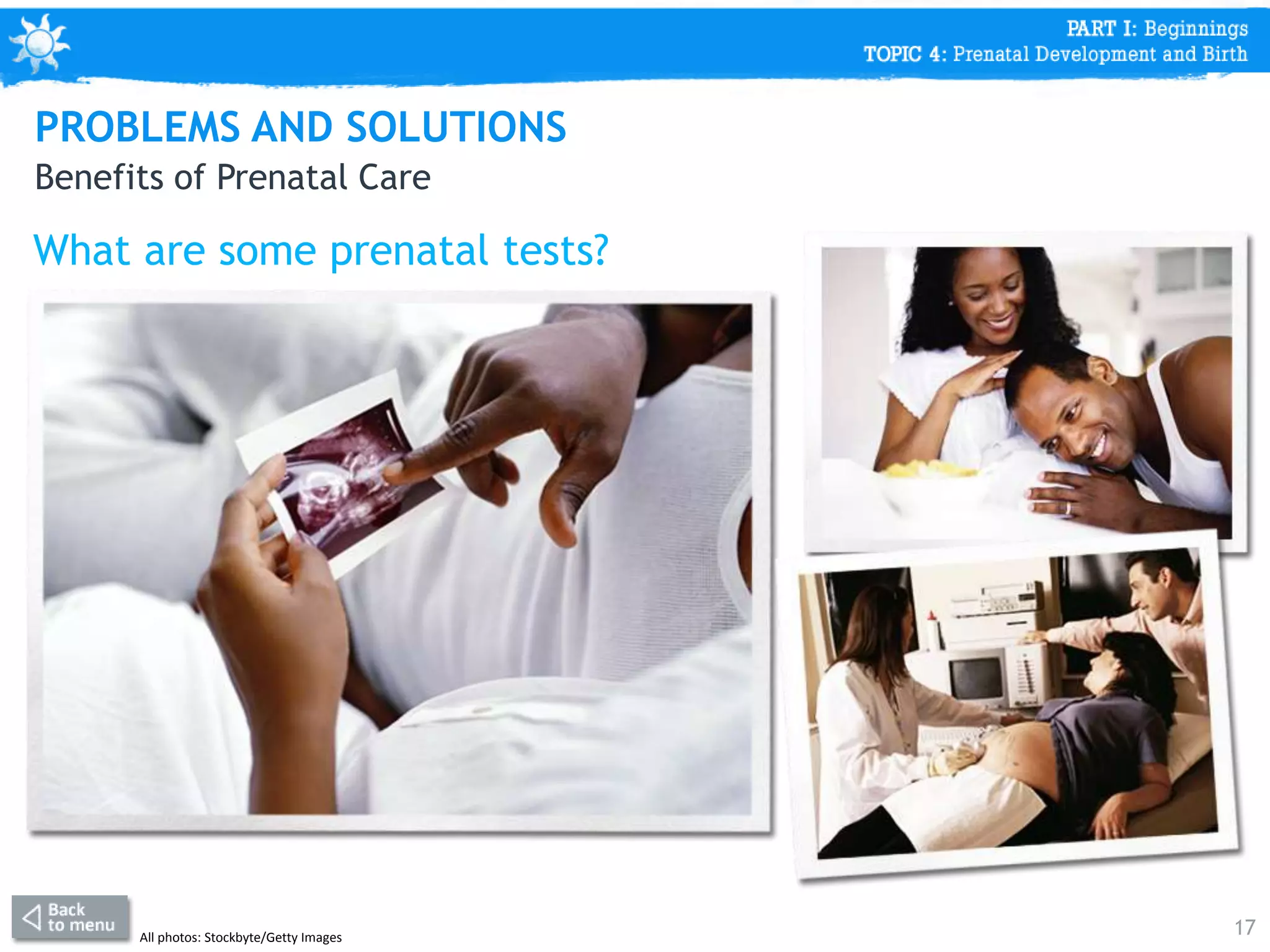
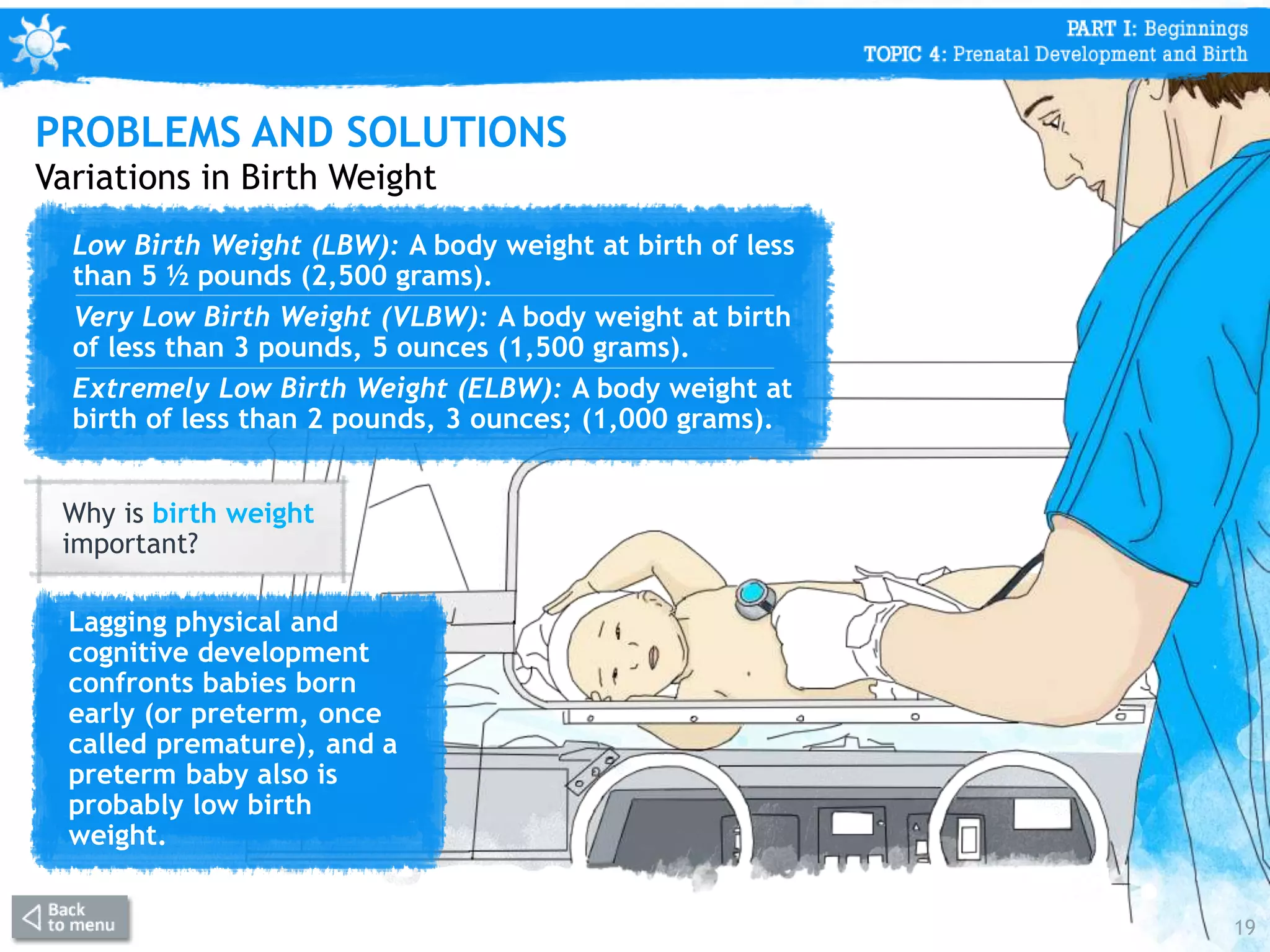
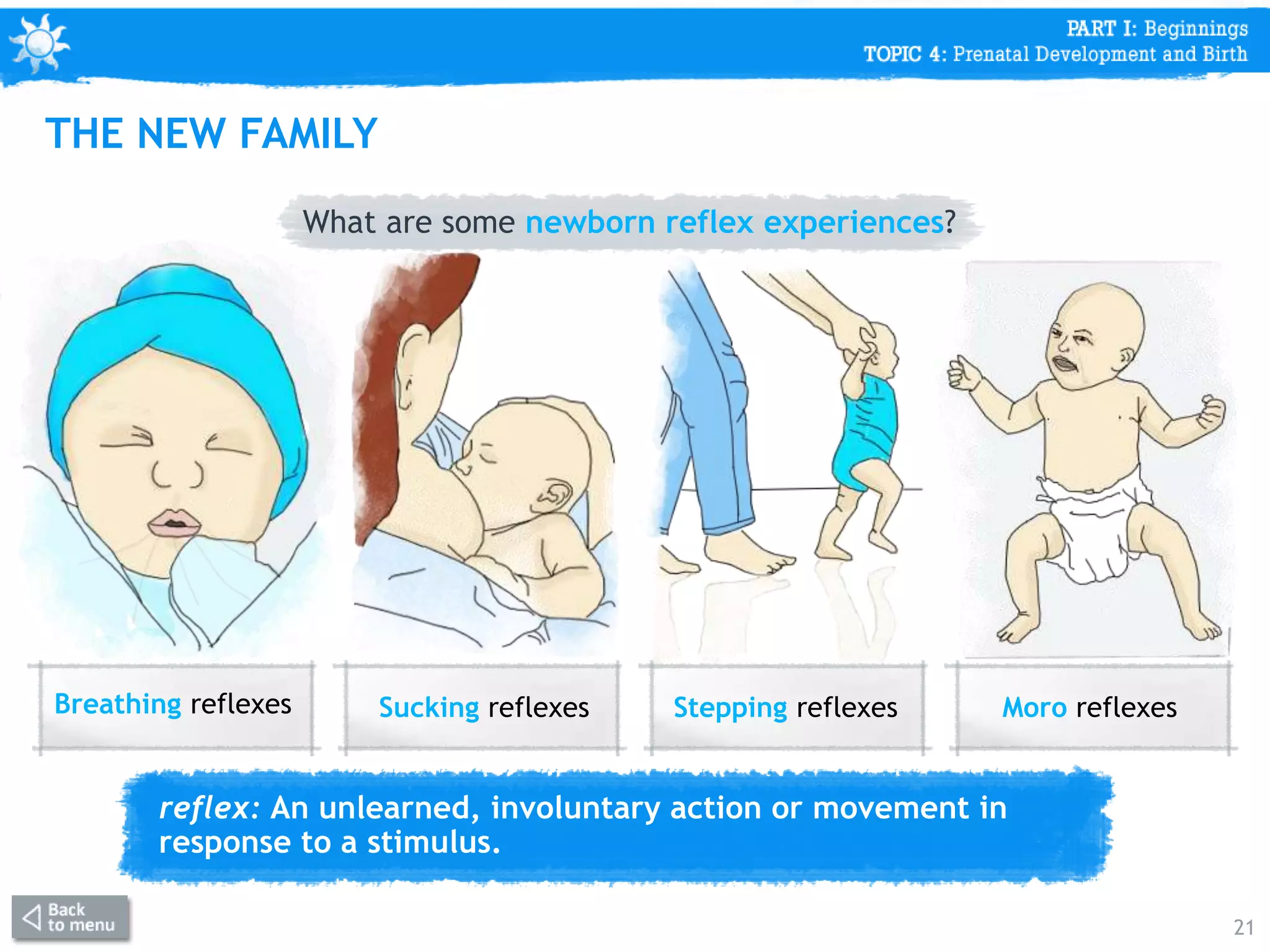
This document discusses prenatal development from conception through birth. It covers topics like the stages of prenatal development (germinal period, embryonic period, fetal period), what happens in each period like organ formation, common tests during pregnancy, risks from teratogens, and complications like low birth weight. The document emphasizes that the prenatal period involves the most dramatic transformation as the embryo and fetus develop all body parts and organ systems before birth.