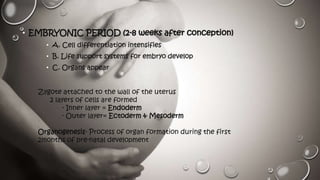
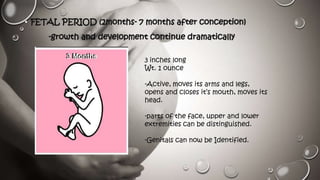
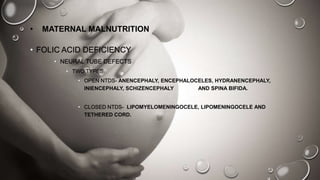
This document discusses pre-natal human development from conception through birth. It describes the stages of development from the germinal period through the fetal period. During these stages, cells differentiate and life support systems develop, organs appear and growth occurs. The document also outlines various teratogens and hazards that can threaten pre-natal development, including prescription drugs, psychoactive substances, environmental toxins, maternal diseases, nutritional deficiencies, and other parental factors. Proper pre-natal care and avoiding hazards can help ensure healthy development.