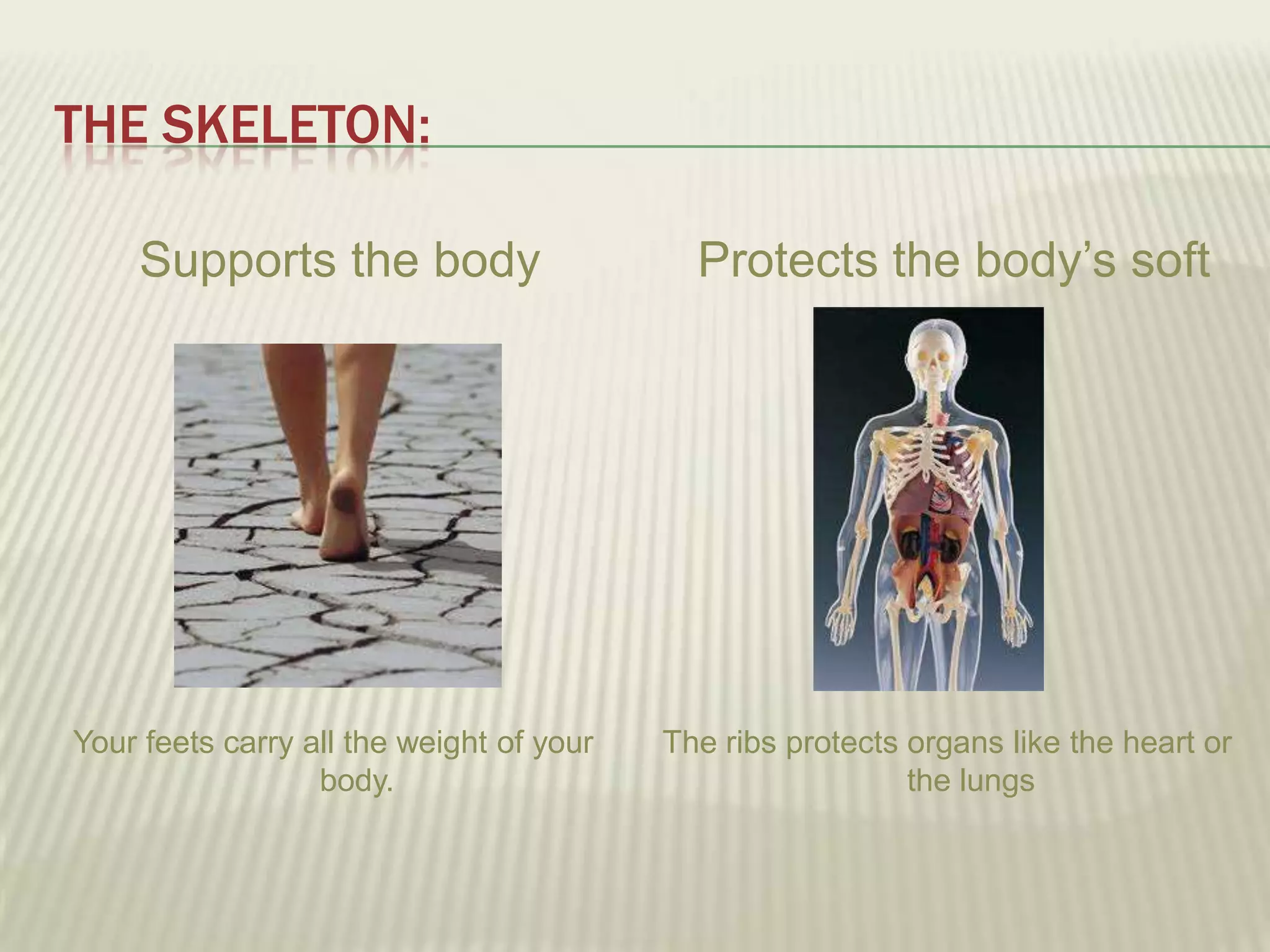
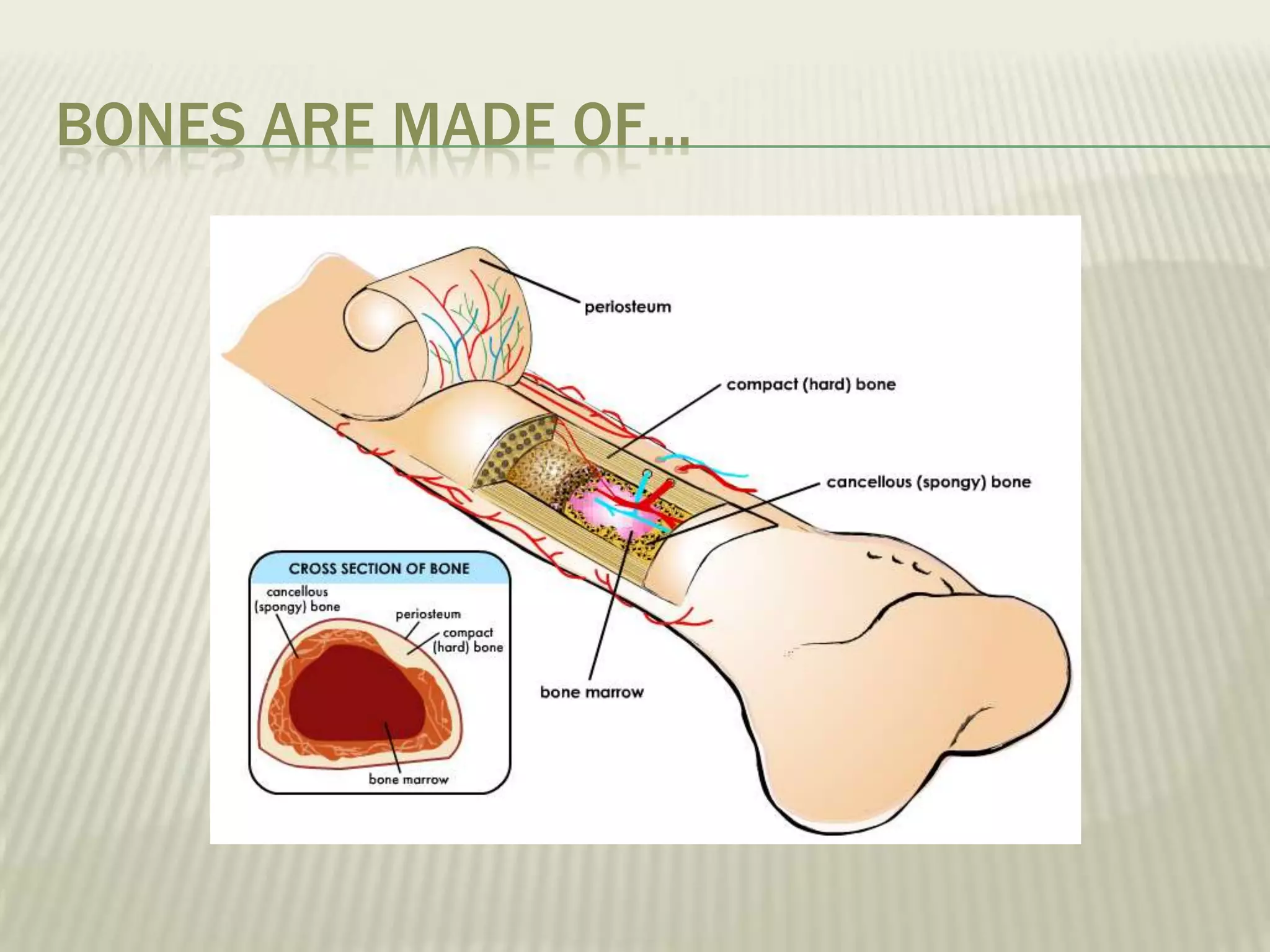
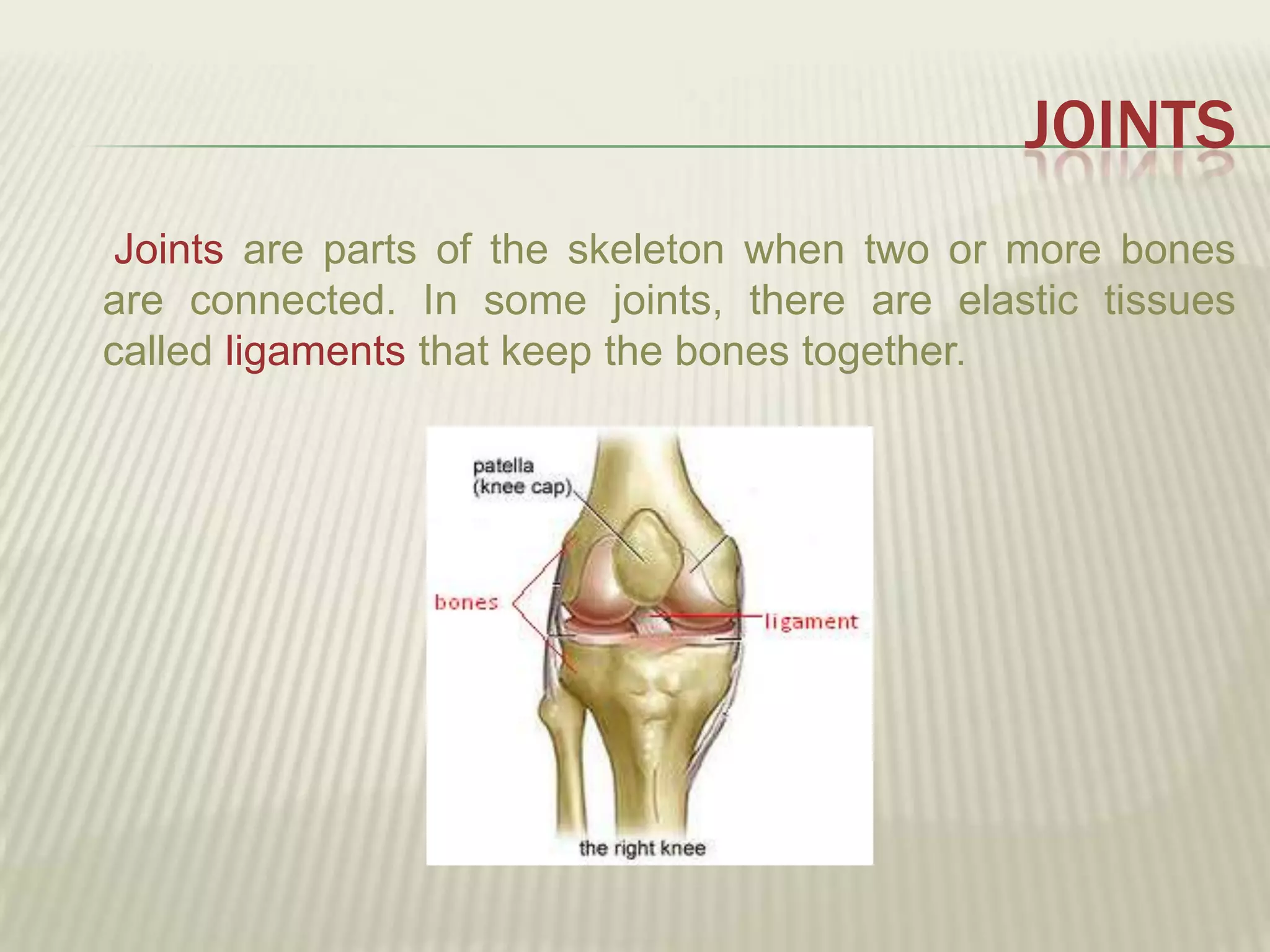
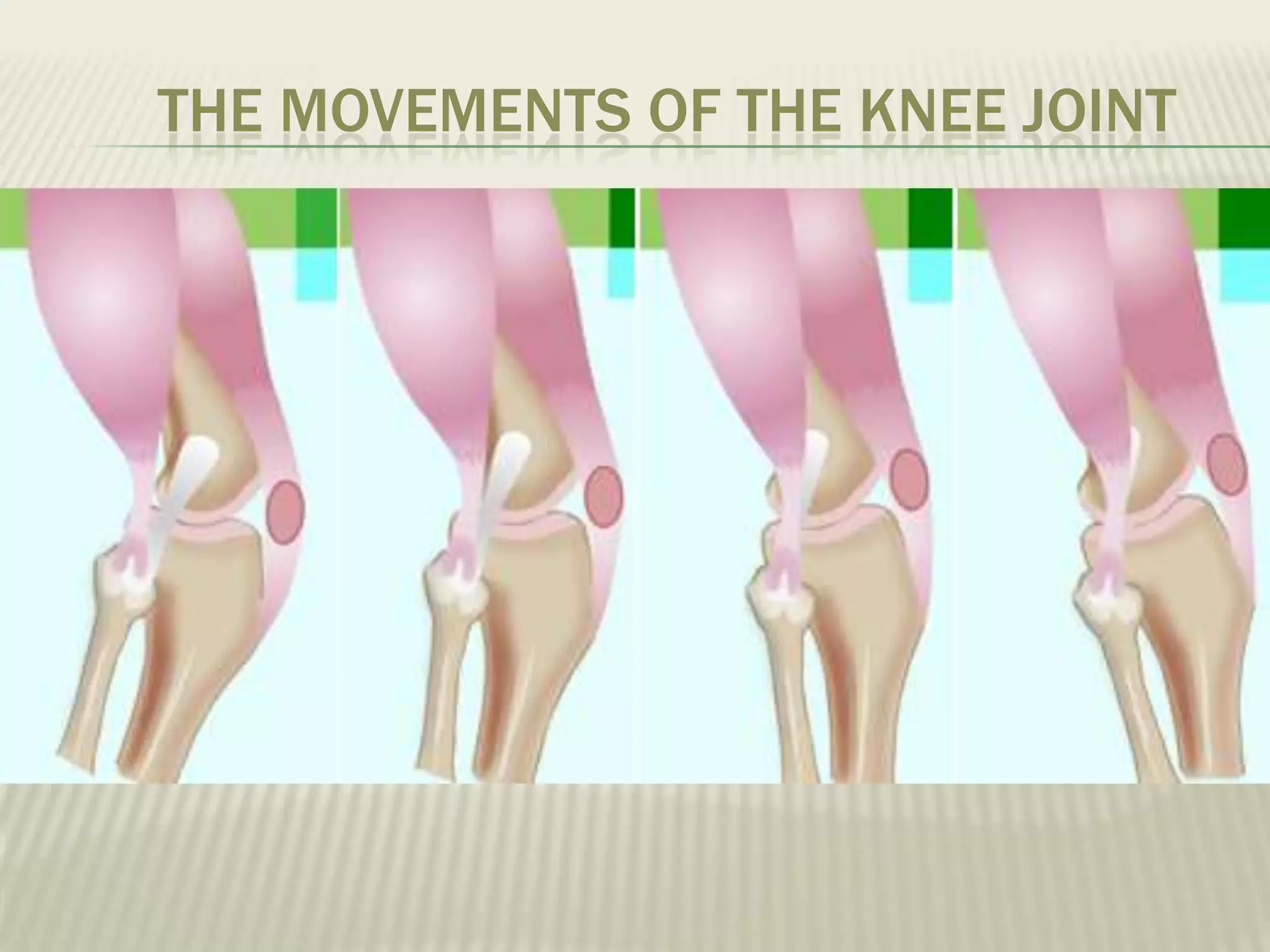
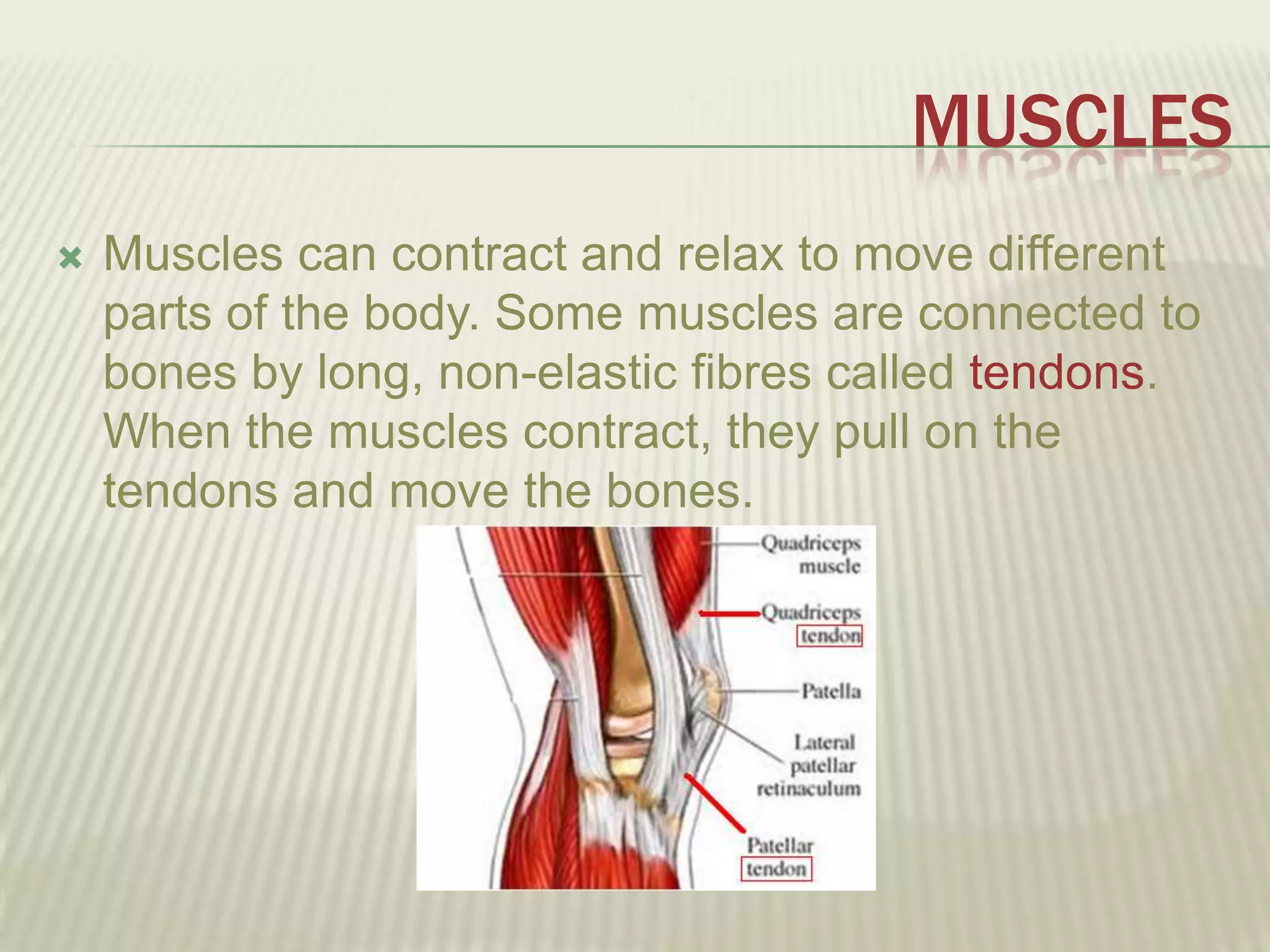
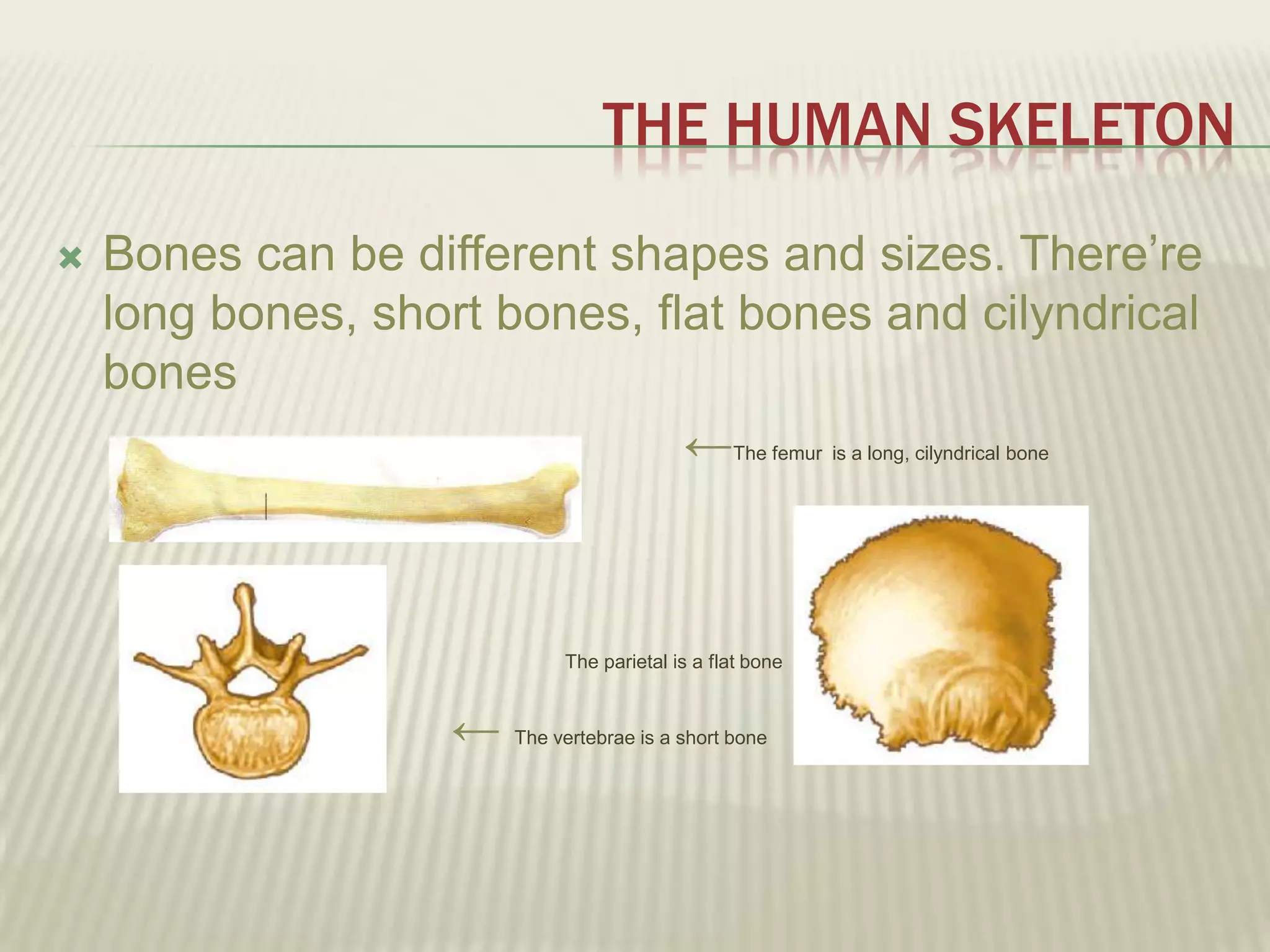
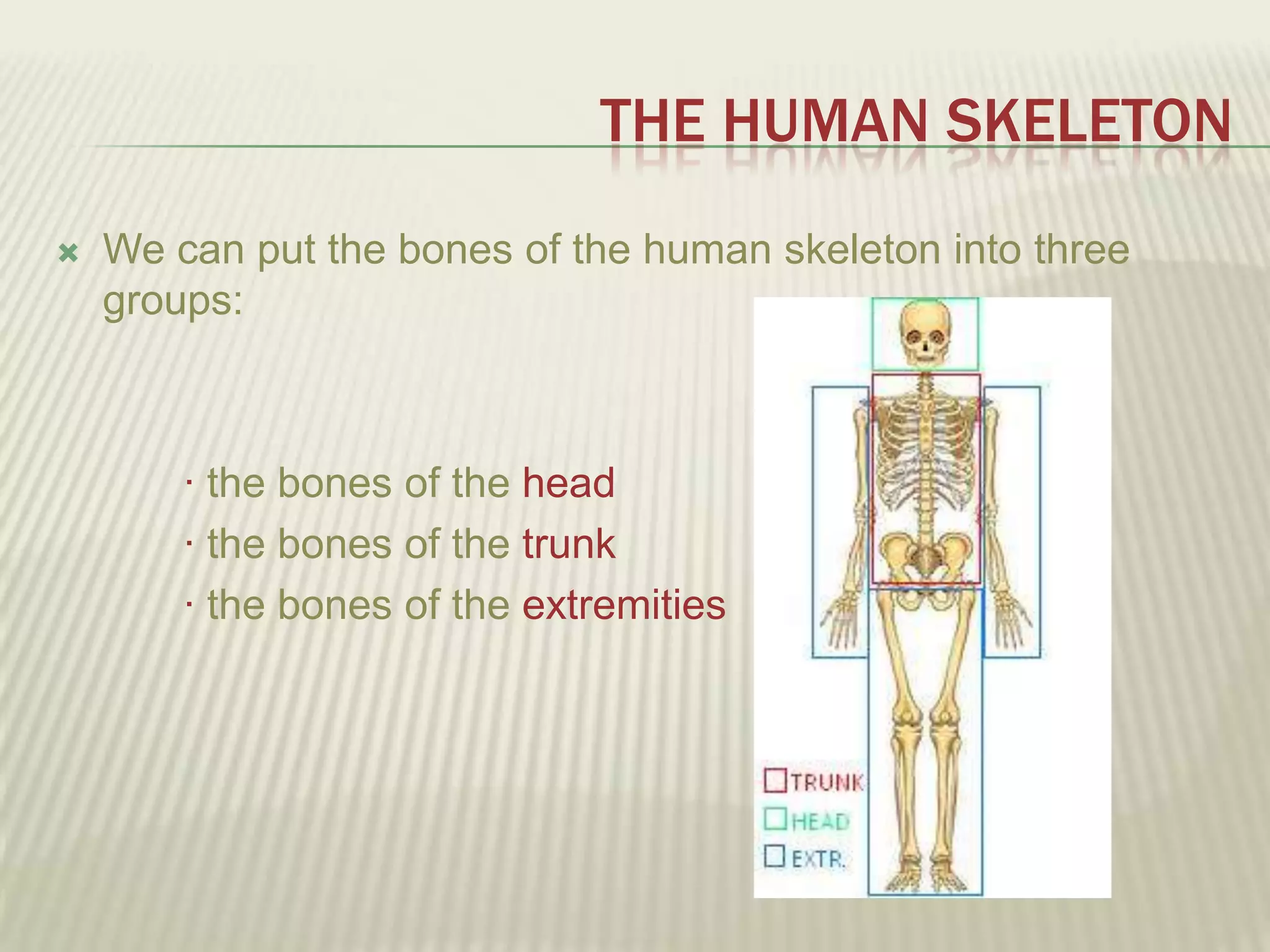
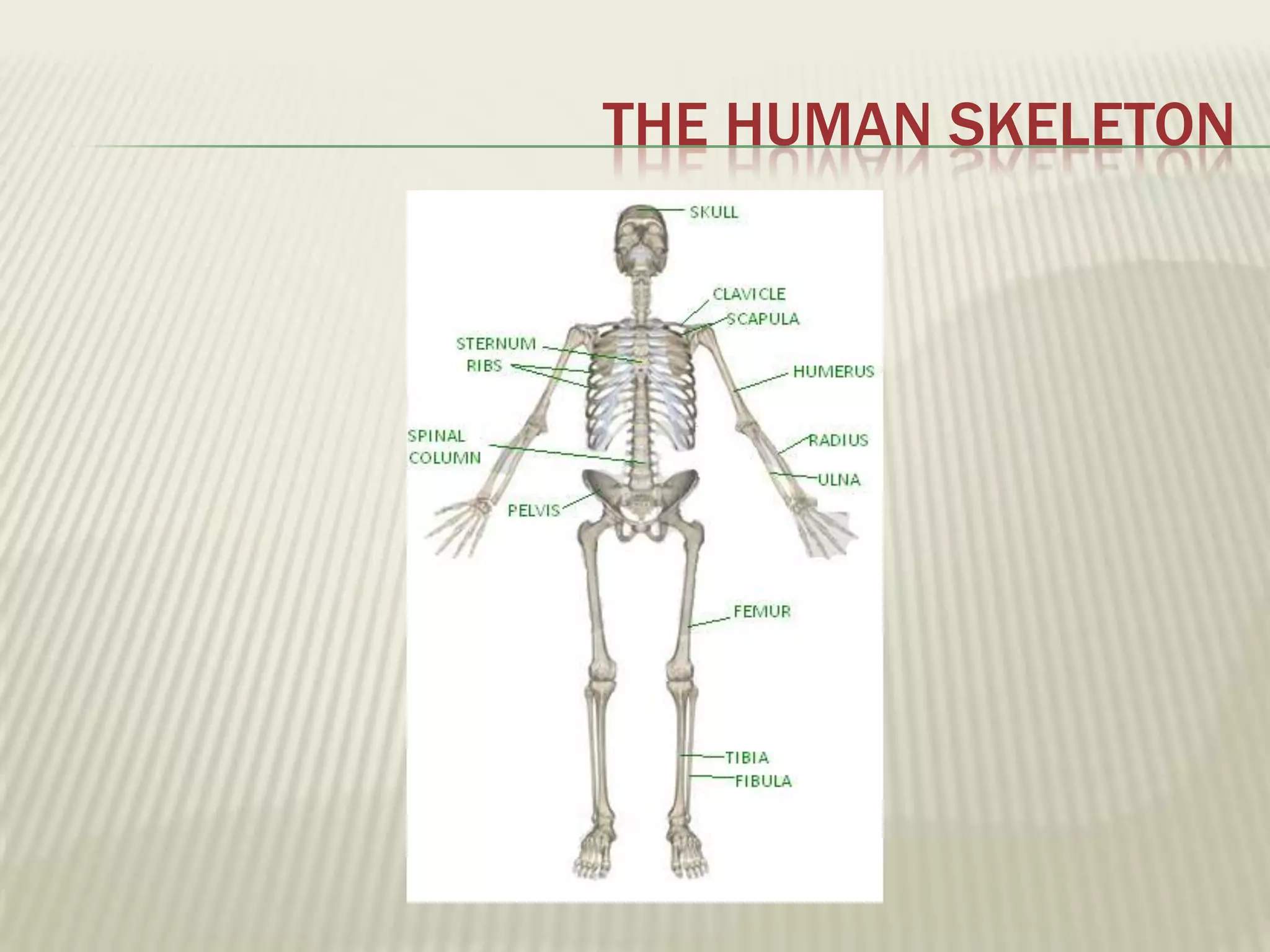
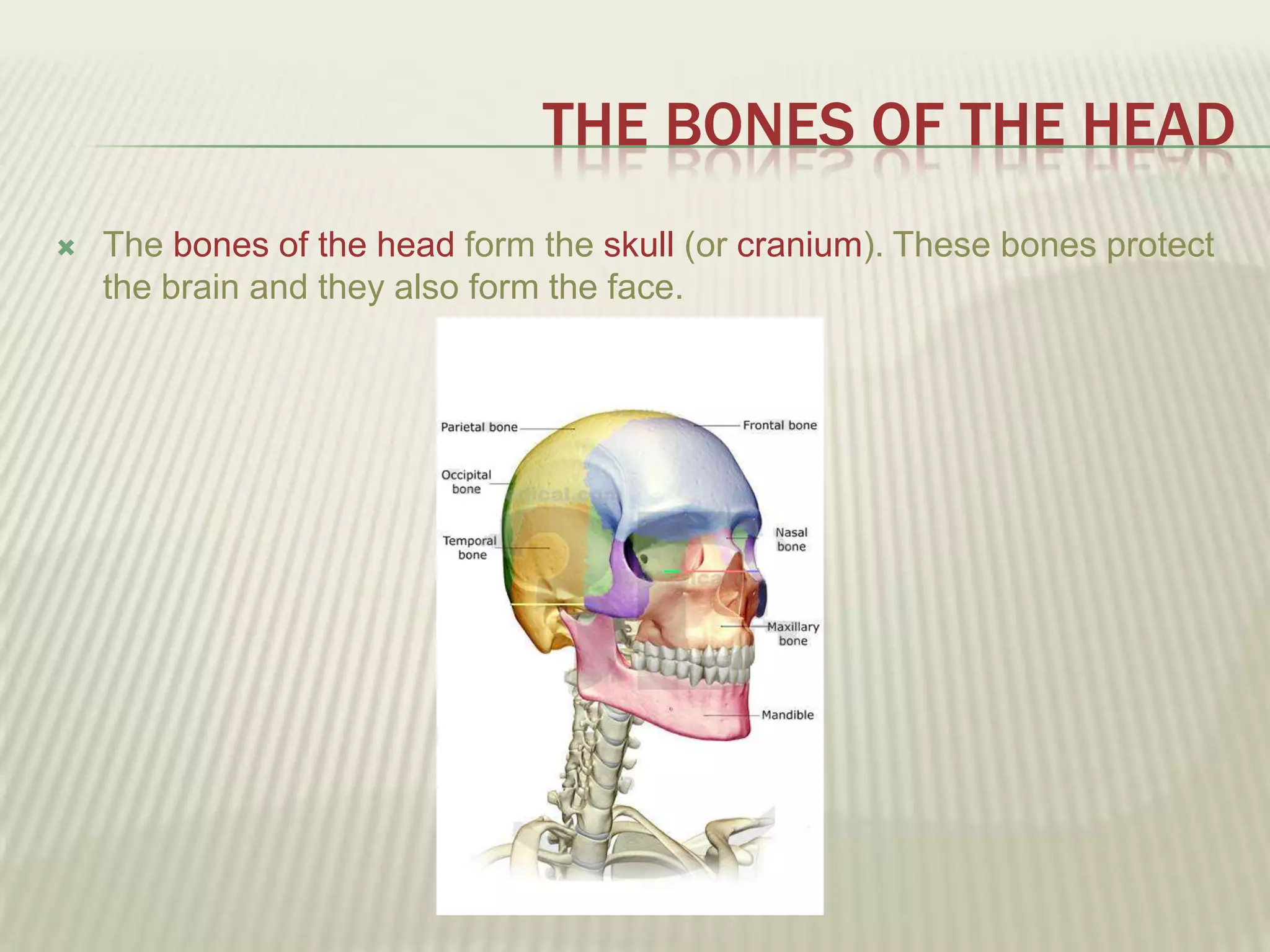
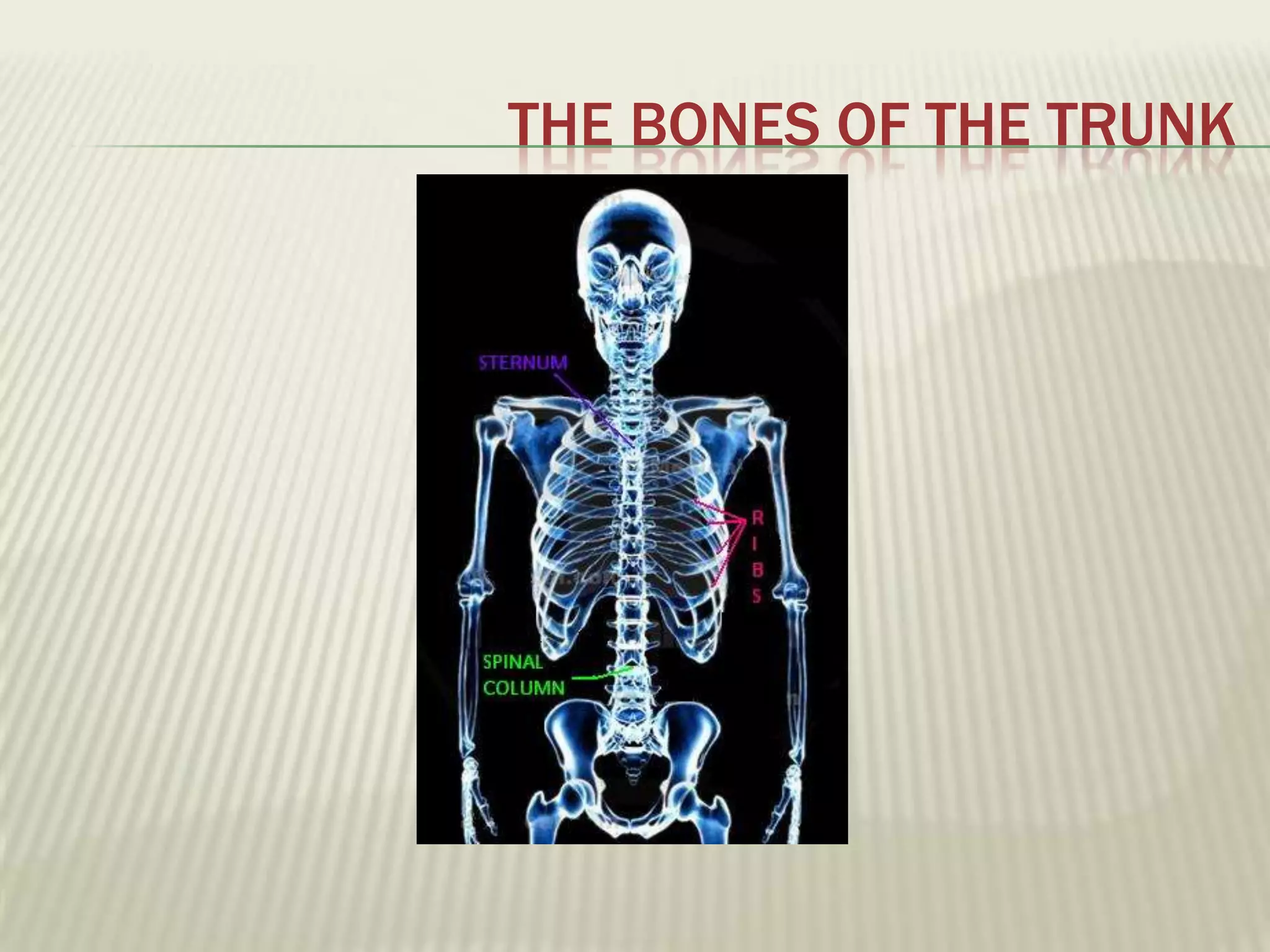
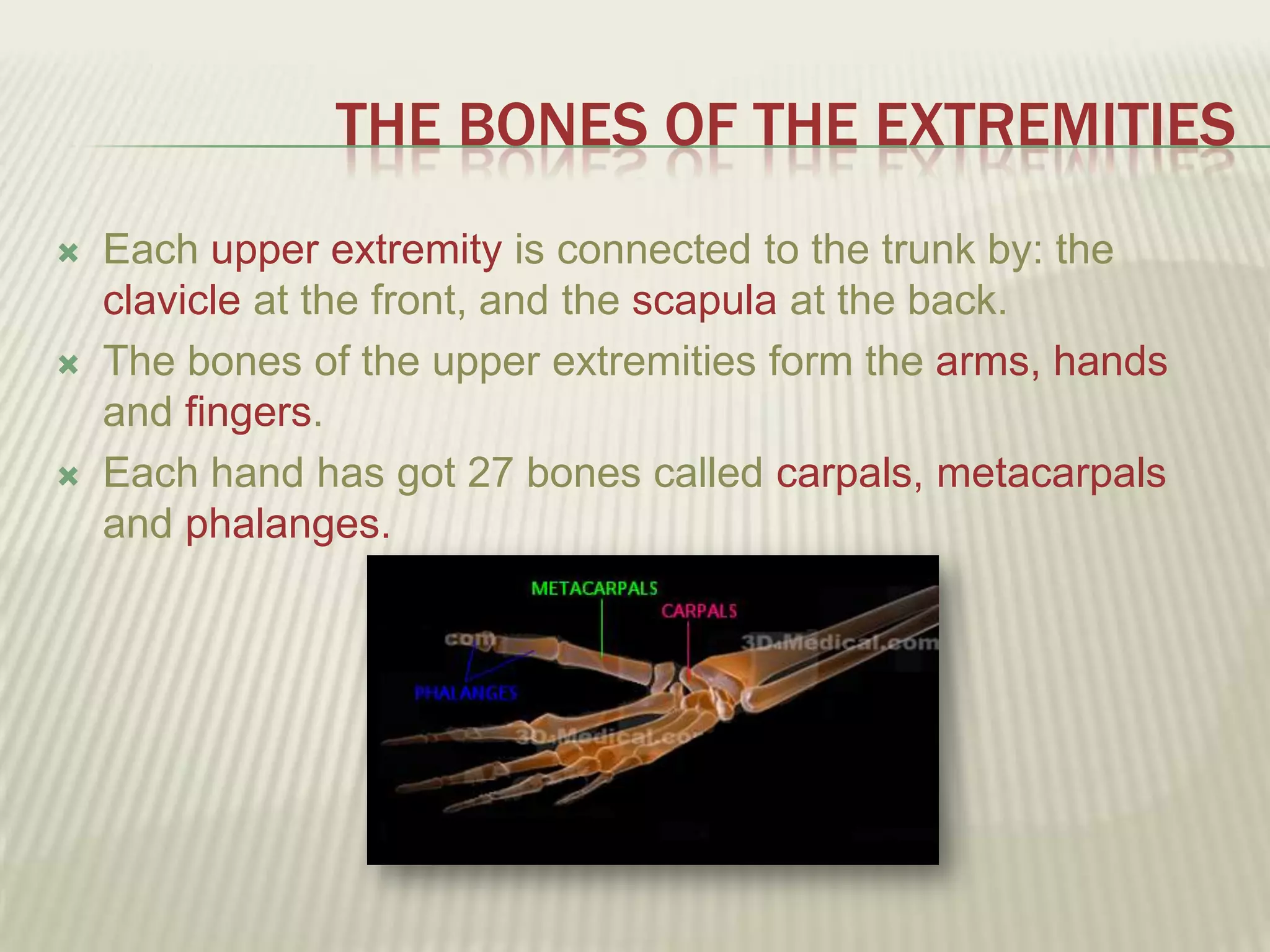
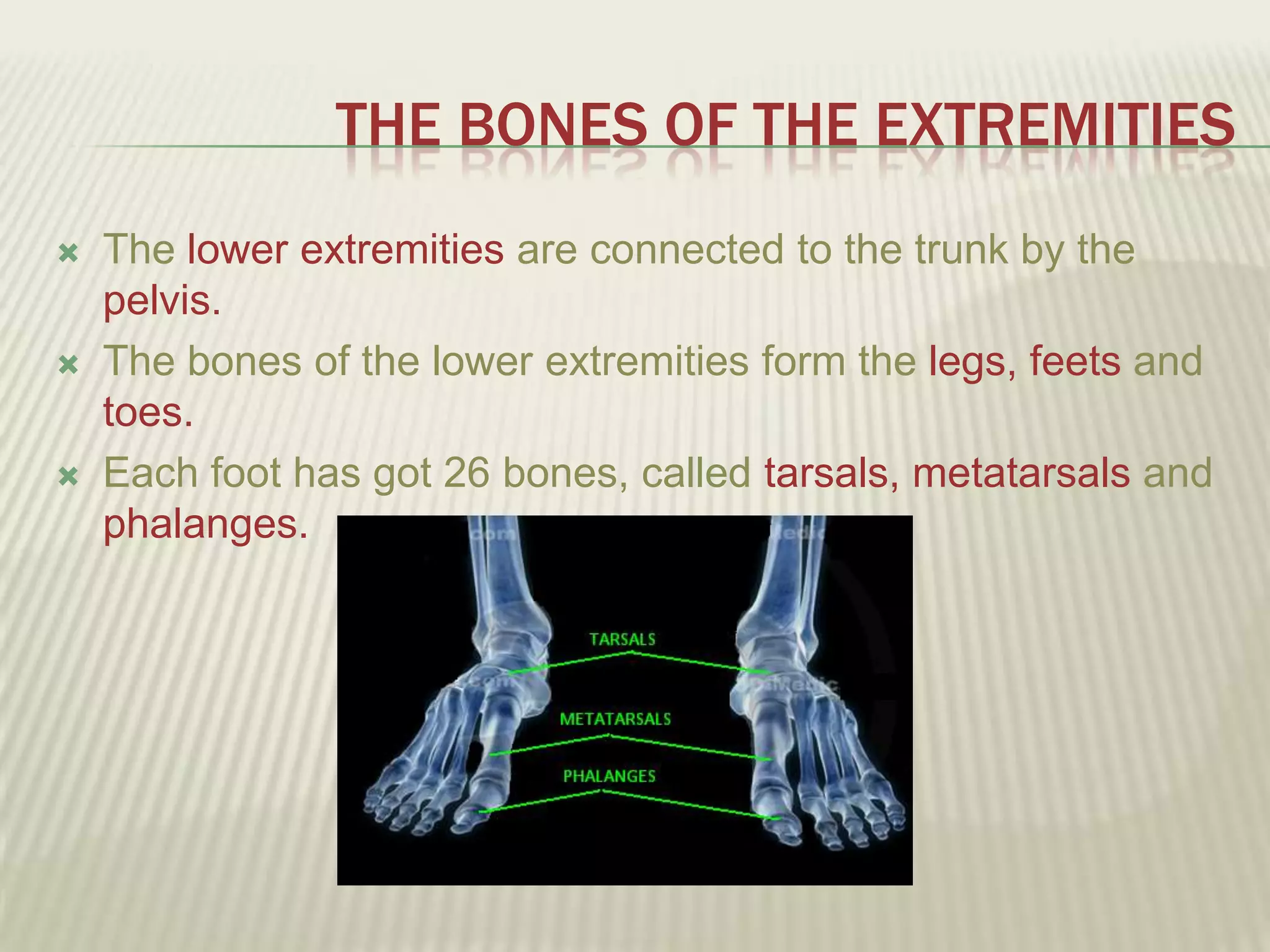
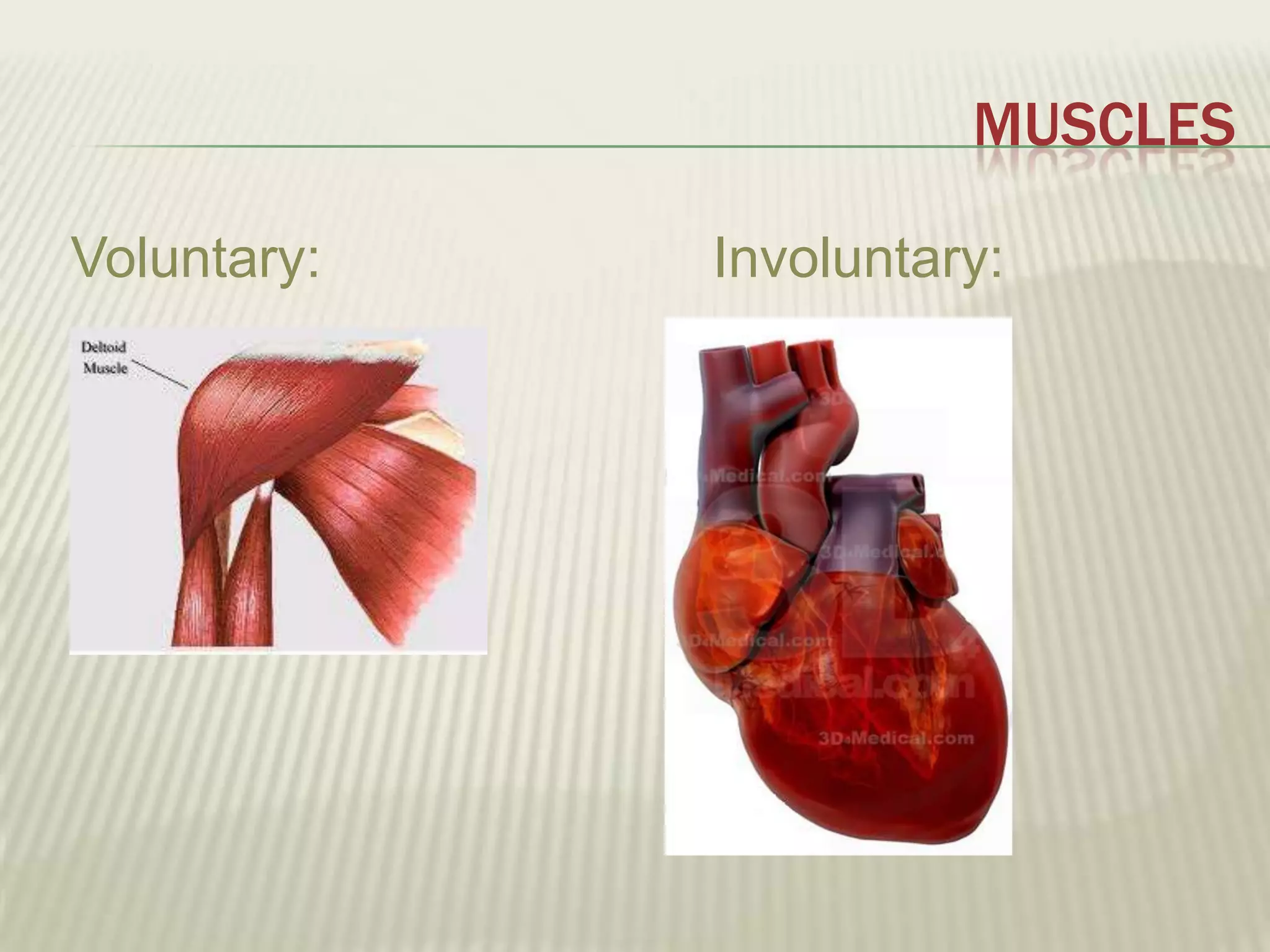
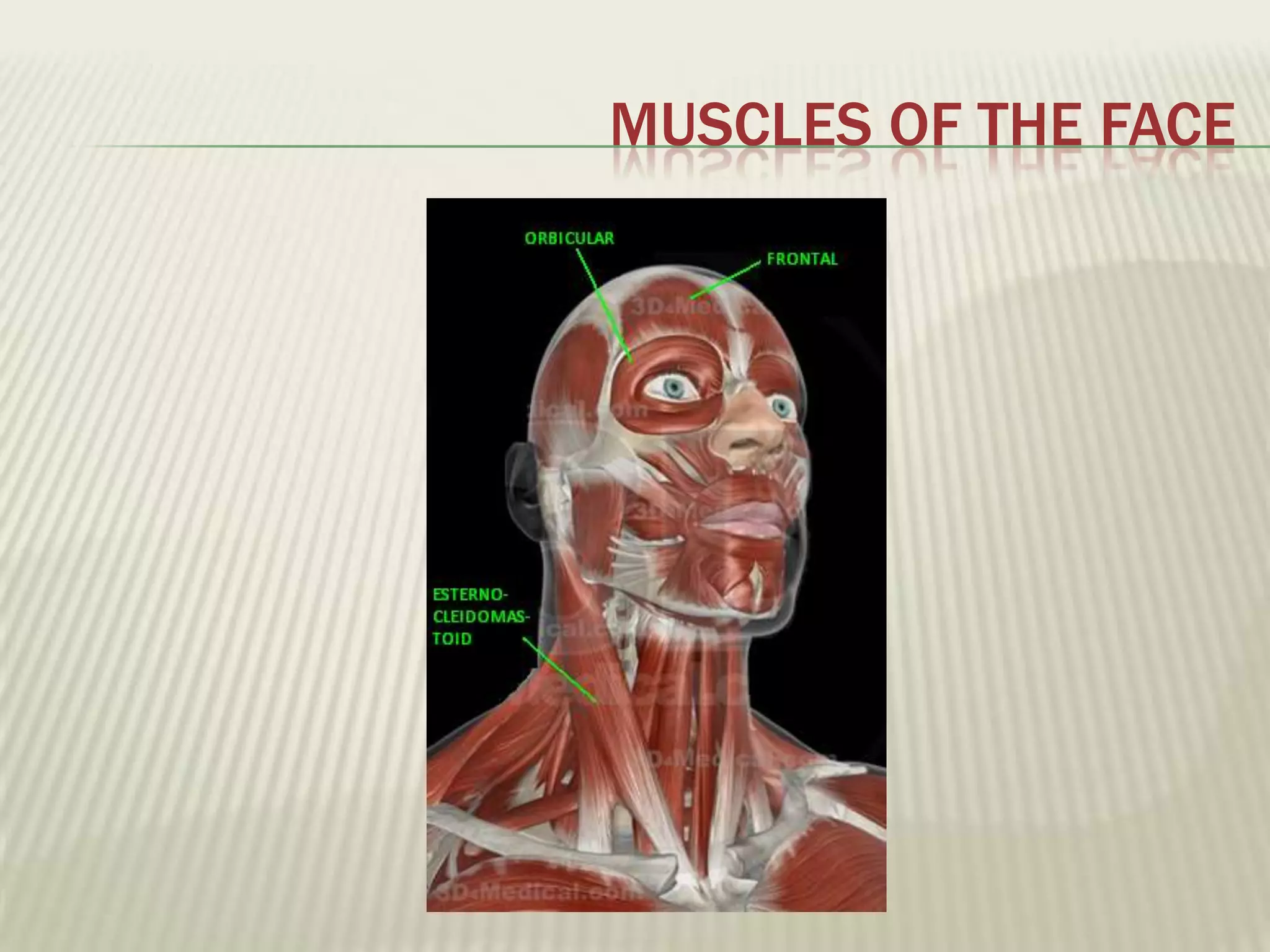
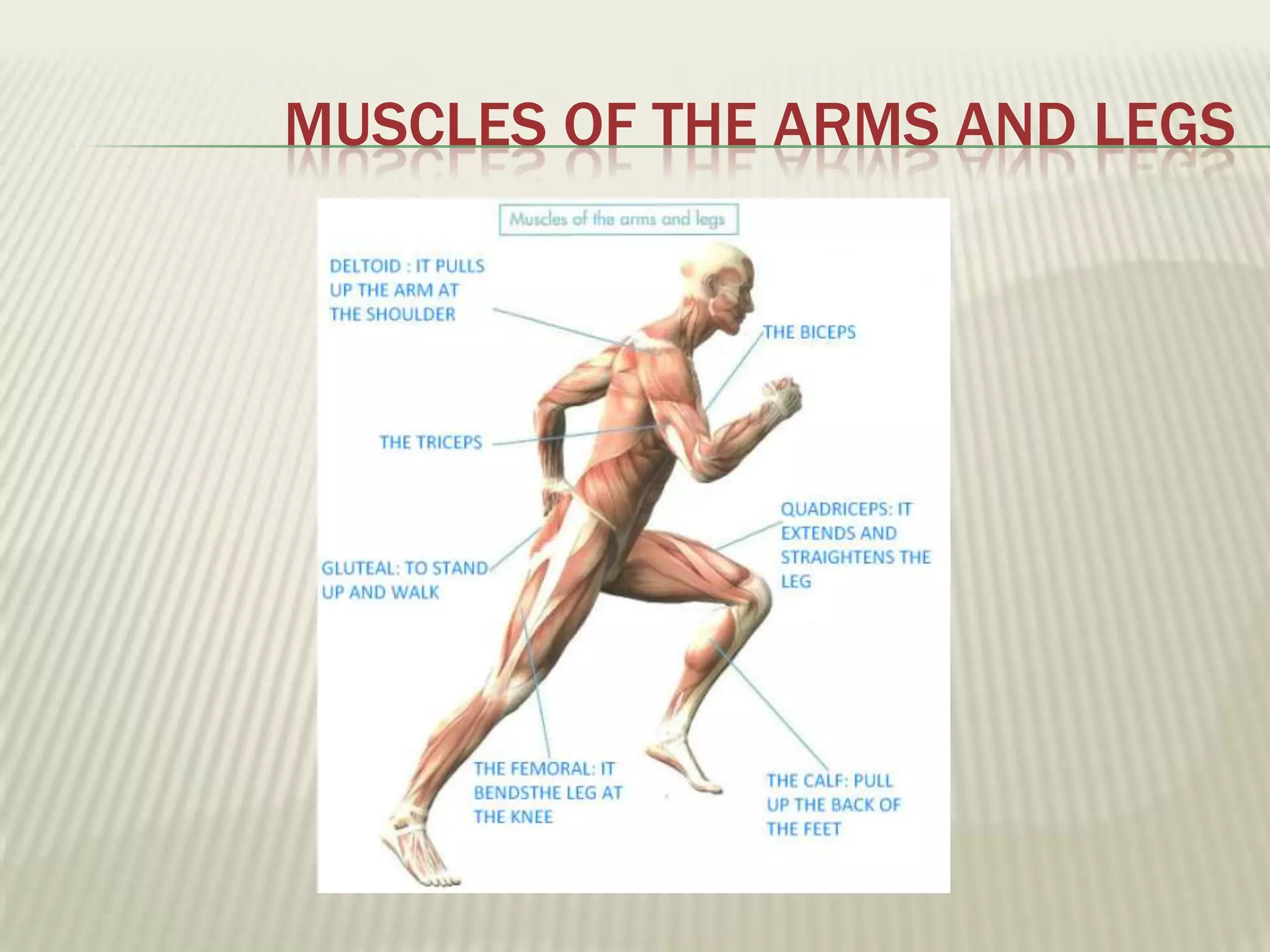
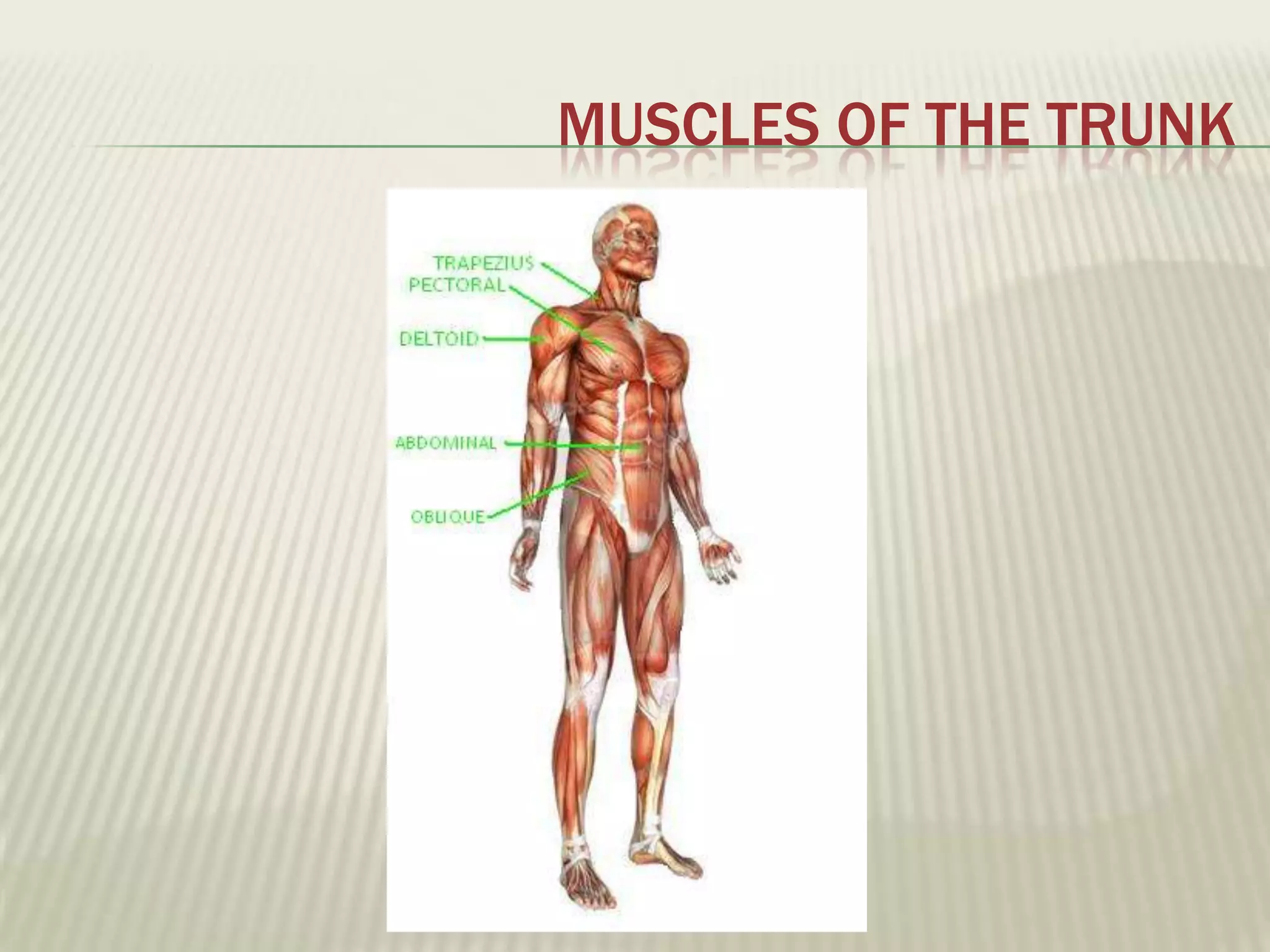
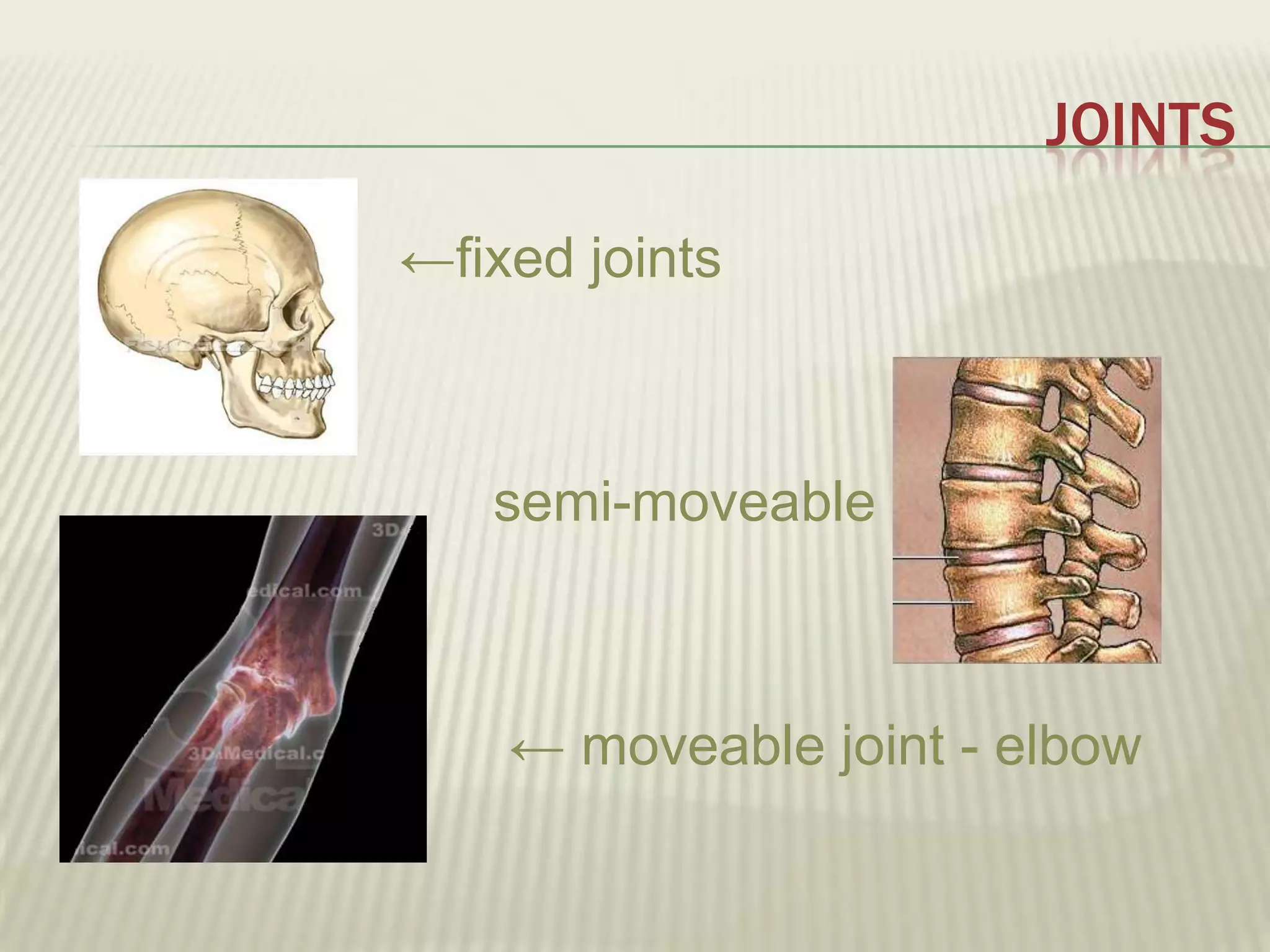
The musculoskeletal system allows humans to move using muscles and bones. It is composed of 206 bones that support the body, protect internal organs, and connect to muscles. Bones come in different shapes and sizes and can be grouped into those in the head, trunk, and extremities. Muscles contract and relax to move bones via tendons. Joints connect bones and vary in mobility. The skeleton and muscles work together to enable movement.