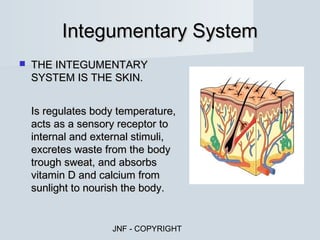
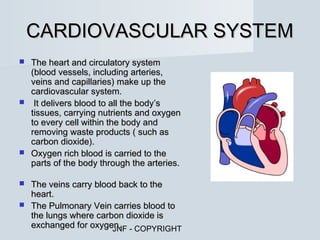
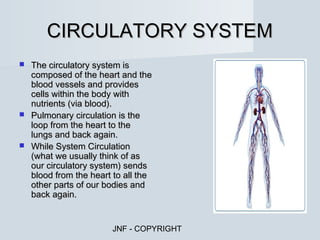
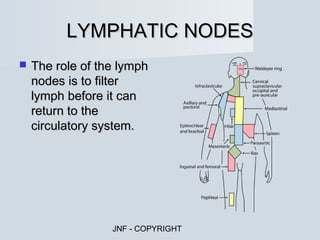
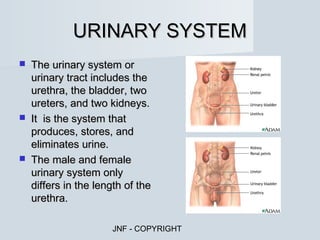
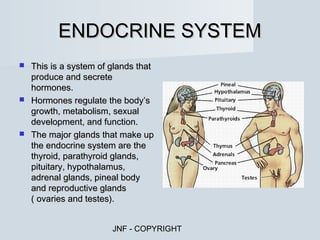
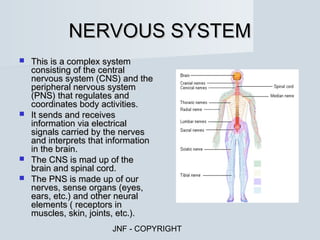
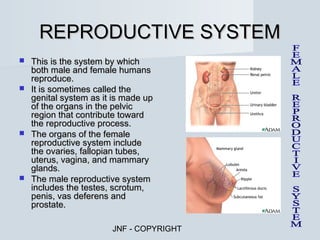
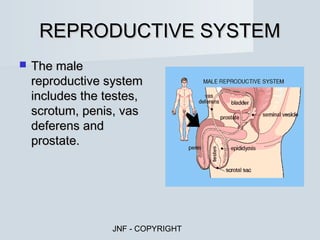
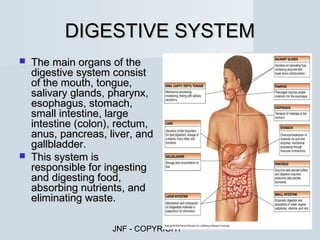
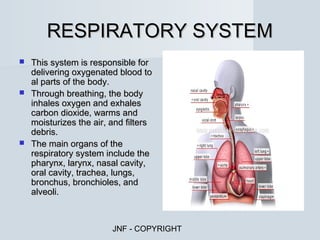
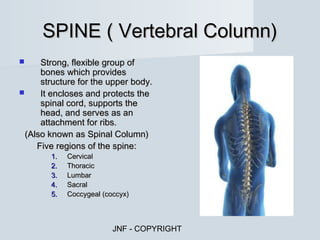
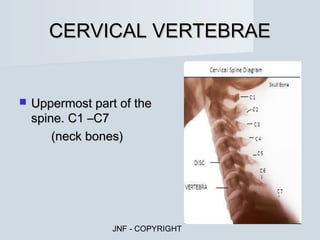
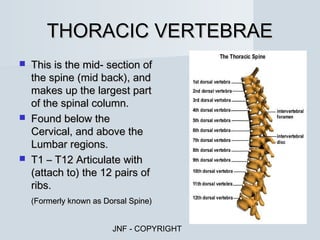
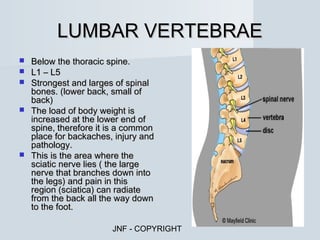
The document describes the major human body systems and their functions. It discusses 11 systems: integumentary, cardiovascular, circulatory, lymphatic, urinary, endocrine, nervous, reproductive, digestive, respiratory, and musculoskeletal. Each system is summarized in 1-2 sentences explaining its main components and role in the body.