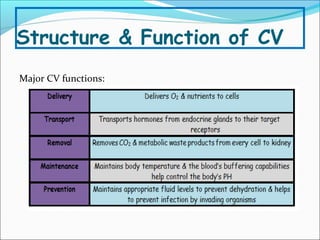
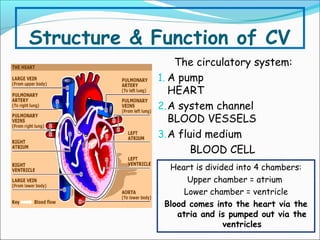
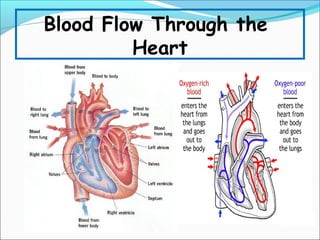
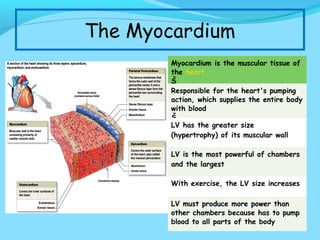
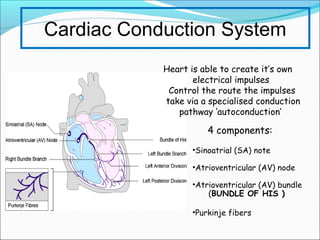
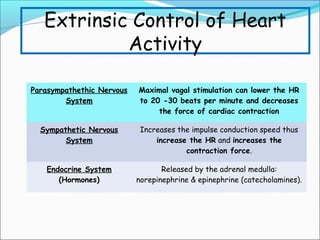
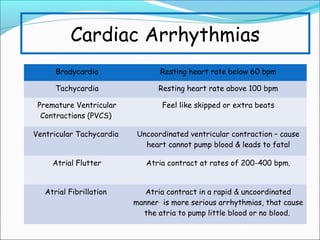
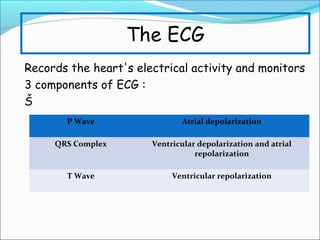
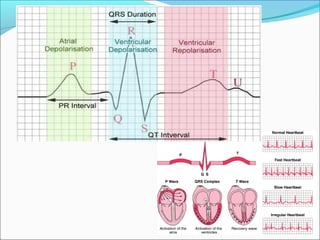
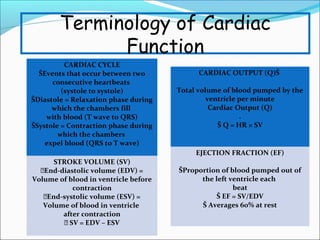
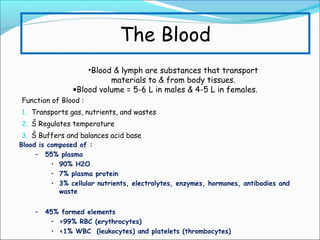
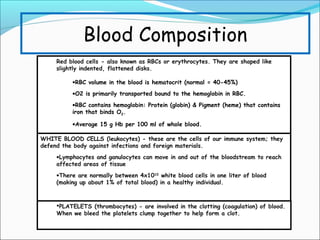
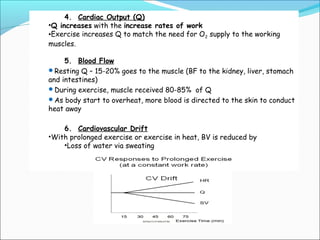
During exercise, the cardiovascular system responds to increase delivery of oxygen and nutrients to working muscles. The heart rate increases to pump more blood with each contraction. The left ventricle increases in size to pump more blood per beat, increasing stroke volume and cardiac output. Blood is redirected away from organs and toward active muscles and skin. Arrhythmias are disruptions to the heart's normal rhythm that can be benign or life-threatening depending on severity. The electrocardiogram monitors the heart's electrical activity through the cardiac cycle.