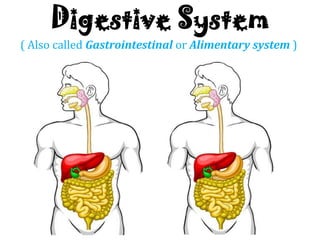
8 3. digestive system
- 1. Digestive System ( Also called Gastrointestinal or Alimentary system )
- 2. • The food we consume will be broken down into nutrient which later can be absorbed by the body • There are 6 nutrients that are needed to keep healthy ; 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fat 3. Protein 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Water Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 3. 1. Carbohydrates • Are a source of energy • Excess carbohydrates will be stored in the liver and muscles • Sources of carbohydrates are rice, corn, sweet potatoes, potatoes, cassavas, etc • 1 gr of carbohydtares provides 4,1 cal. • In the digestion process, carbohydrates are brokendown into simple saccharides or monosaccharides • The body will then absorb these monosaccharides Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 4. • If we consume more carbohydrates more than our body needs, the excess will be converted to glycogen or fat • Glycogen will be stored in the liver or muscles • Fat will be stored in areas around the waist, around the kidneys, and under the skin • Lack of carbohydrates will cause the body to be thin and weak, and it will cause a lack of energy, anxiety, and reduced body immunity Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 5. There are 3 kinds of carbohydrates, they are ; 1. Monosaccharides carbohydrates that consist of 1 simple sugar they are glucose, fructose, galactose 2. Disaccharides carbohydrates that consist of 2 simple sugars they are ; a. Maltose = glucose + glucose b. Sucrose = glucose + fructose c. Lactose = glucose + galactose Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 6. 3. Polisaccharides carbohydrates that consist of many simple sugars for example, rice, bread, potatoes, etc Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 7. 2. Fat • Its function as a source of energy • 1 gr of fat provides 9,3 cal • Fat is acquired from both animals and plants • Fat that is acquired from animals is called animal fat, for ex. Butter, milk, meat, eggs, etc • Fat that is acquired from plants is called vegetable oil, coconuts, candlenuts, peanuts, avocado, etc Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 8. • In the digestion process, fat is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol with the help of the enzymes • Fat also has other function ; a. As a food store, that is stored under the skin b. Protect vital organs c. As an insulator and prevents the loss of body heat d. Helps to dissolve vitamin A, D, E, and K so that they can be easily absorbed. Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 9. 3. Protein • The main function of protein is for the formation of the body’s main structure, cell regeneration, and coordination of biological processes in the body • 1 gr of protein provides 5,3 cal. • Proteins are acquired from both animals and plants, that are acquired from animals are called animal proteins (meat, fish, egg, etc) and that are acquired from plants are called vegetable proteins (soybeans, peanuts, green beans, etc) Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 10. 4. Vitamins • Vitamins are needed only in small amounts, but lack of one of vitamins can cause avitaminosis. • Vitamins act as coenzymes (biocatalysts), substances that help accelerate chemical reactions in the body. • Based on their solubility, vitamins are classified into water- soluble and fat-soluble vitamins. a. Water-soluble vitamins are vitamin B and C. These vitamins can not be stored in the body, which means that the body will only use as much as it needs and excretes the rest. b. Fat-soluble vitamins are vitamin A, D, E and K Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 11. 5. Dietary Minerals • Minerals are needed only in small amounts • Each mineral has certain functions in the body, and lack of a mineral is called mineral deficiency • Examples of dietary minerals needed by the body are as follows ; 1. Calcium (Ca) 2. Iron (Fe) 3. Iodine (I) 4. Phosporus (P) 5. Potassium (K) 6. Sodium (Na) 7. Fluorine (F) Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 12. 6. Water • Water is the main component of protoplasm • The human body contains 60% of water • In the body, water has the role of ; a. Dissolving nutrients and accelerating chemical reactions b. Carrying metabolic waste c. Carrying other bodily substances d. Forming body fluids e. Regulating body heat Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 13. The human body’s “gastrointestinal tract” or “alimentary canal” is up to 10m long Along this pathway: Ingestion Digestion Absorption Egestion About 95% of ingested food is absorbed and made available to our body, the rest is egested Digestion is the breakdown of substances (other organisms!) into small molecules that can be absorbed by cells There are two ways of digestion ; Physical/Mechanical Chemical Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 14. The 2 ways of digestion Mechanical Chemical Changes the physical form of food Changes the chemical composition Chew of food with the aid of digestive Tear enzymes Grind • Lipids to fatty acids Mash • Proteins to individual amino Mix acids The breakdown of food into small • Carbohydrates into simple sugars pieces without chemically changing them into different substances Helps facilitate chemical digestion by Digestive enzymes are special increasing surface area proteins that help break up large Increased surface area exposes food molecules of food into very tiny pieces to enzymes and other substrate molecules and increases molecules that can be absorbed the rate of metabolic reactions and used by the cells in the form of Examples: teeth, stomach (HCl), nutrition. intestines (bile) Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 15. 6 Functions of the Digestive System 1. Ingestion: occurs when materials enter digestive tract via the mouth 2. Mechanical processing: crushing and shearing makes materials easier to propel along digestive tract 3. Digestion: is the chemical breakdown of food into small organic fragments for absorption by digestive epithelium Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 16. 4. Secretion is the release of water, acids, enzymes, buffers, and salts by epithelium of digestive tract by glandular organs 5. Absorption movement of organic substrates, electrolytes, vitamins, and water across digestive epithelium into interstitial fluid of digestive tract 6. Excretion removal of waste products from body fluids Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 17. Components of the Digestive System Digestive Tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract divided into: Alimentary canal. Accessory digestive organs. Is a muscular tube Extends from oral cavity to anus Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 18. • Your digestive tracts or food tube consist of the following: (1) mouth (2) esophagus (3) stomach (4) small intestine (5) large intestine (6) Anus • The accessory organs are : (1) salivary glands (2) pancreas (3) liver (4) gallbladder Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 19. The Organs of Digestive System movie Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 20. Digestion from the Mouth • Saliva – lubricates the food and secretes an enzyme, ptyalin or salivary amylase, that convert starch to maltose • 3 Salivary Glands • Parotid glands • Submaxillary glands • Sublingual glands Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 21. • Tongue – pushes the food to the back of your mouth • Bolus – a soft, mass of rounded ball of food that is being chewed Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 22. Digestion from the Esophagus • Pharynx – an alimentary canal where food goes down after the digestion in the mouth • Epiglottis- a flap of tissue that closes over the trachea to prevent the food from entering • Esophagus – carries the food down the stomach Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 23. Digestion from the Stomach Stomach a large J-shape organ found at the end of the esophagus contraction of the muscles of the stomach causes the churning, squeezing and twisting effect it where partial digestion of food happens Cardiac spincter – closes and opens to allow the flow of food from the esophagus to the stomach Pepsin – enzymes secreted in the stomach that breaks down the protein Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 24. • Pyloric valve or spincter – opens and closes to allow the food getting in the small intestine • Chyme – partial product retained in the stomach before transferring into the small intestine Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 25. Digestion from the Small Intestine • 3 Major Parts 1.duodenum – upper 20 cm 2. jejunum – 2.5 meters long 3. ileum – longest half coiled into the abdominal cavity • It is where the final digestion and absorption of food take place • Villi – small finger-like projection in the lining of the small intestine that is used in absorption • Maltase – enzymes that break down maltose into glucose Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 26. PANCREAS • Pancreas – a digestive gland that serves 2 functions: 1. secrete hormones that regulate blood glucose 2. secretes pancreatic juice that netralizes the acid in the stomach Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 27. LIVER • The liver is the largest gland in our body that carries the gall bladder Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 28. GALL BLADDER • Gall bladder – Produces a blue green fluid called bile Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 29. The Gallbladder Movie Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 30. LARGE INTESTINE • Undigested food goes down into the large intestine • It is where the absorption of water is happen • It is also called as colon FECES – remaining food material Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 31. RECTUM AND ANUS Rectum • 20 to 30 cm • a muscular cavity where feces is temporarily stored Anus – end of the alimentary canal Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 32. The Digestive System movie Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 33. The Digestive System Diseases Appendicitis the inflammation of the appendix may cause inflammation of the diaphragm membrane the basic treatment of appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix appendectomy Constipation the delayed passage of waste continuous constipation may be a symptom of other diseases will cause irregular defecation and headache Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
- 34. Parotitis or Mumps is a feverish cold caused by virus, soon followed by swelling and stiffening in the region of the parotid salivary glands in front of the ear if you suffer mumps, take a vitamin C supplement and consult a doctor Xerostomia is a disease that infects the oral cavity It may cause dry mouth due to the distrubed production of saliva, which will later affect the food processing in the mouth Created By Alfi Msk _ A biology Teacher of GIS JH
