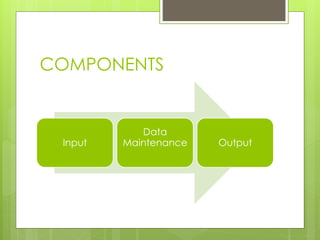
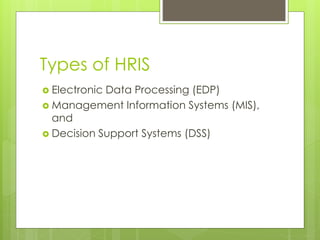
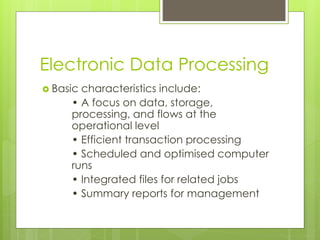
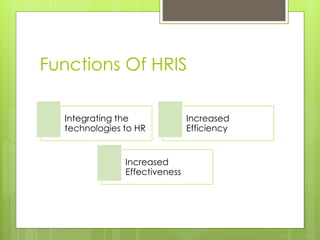
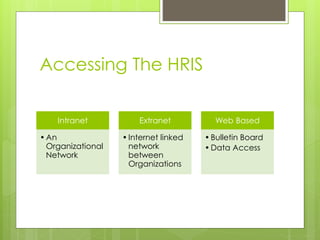
An HRIS is a system that acquires, stores, manipulates, analyzes, retrieves, and distributes information about an organization's human resources. It includes hardware, software, people, forms, policies, and data. There are three main types of HRIS: electronic data processing systems focused on operational data storage and processing; management information systems aimed at middle management with integrated and structured information flows; and decision support systems focused on flexibility for top executives. An HRIS can increase efficiency by allowing more transactions with fewer resources and increase effectiveness by improving the accuracy of information or simplifying processes.