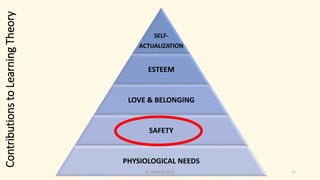
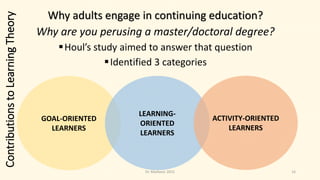
This document summarizes key concepts in andragogy, the study of adult learning. It discusses how ancient teachers taught adults through techniques like Socratic dialogue and case studies. It outlines Eduard Lindeman's six assumptions of adult learning, including that adults are motivated by life needs and interests and draw from life experiences. Theories that contributed to learning theory are explored, such as those from Freud, Dewey, Maslow and Rogers. Pedagogy and andragogy are contrasted based on differences in learners' needs, self-concept, experience, readiness, orientation and motivation.