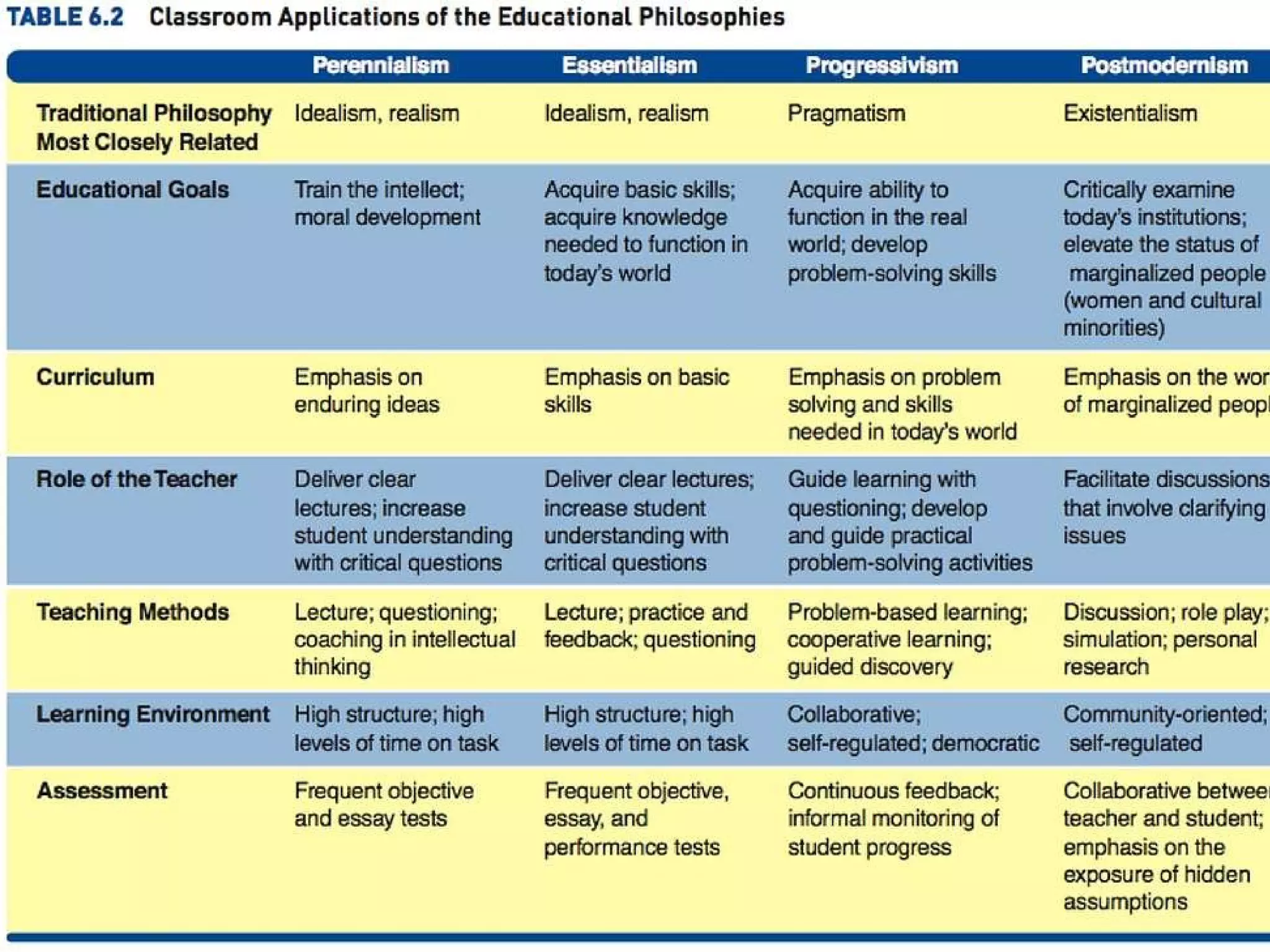
This document provides an overview of different philosophies of education including idealism, realism, pragmatism, and existentialism. It discusses key philosophers associated with each approach and how each philosophy influences teaching practices. The document encourages readers to reflect on which philosophy aligns most with their own views as a student, parent or teacher. It also briefly outlines additional philosophies of education like perennialism, essentialism, progressivism, and postmodernism. Readers are then instructed to develop their own statement of educational philosophy.