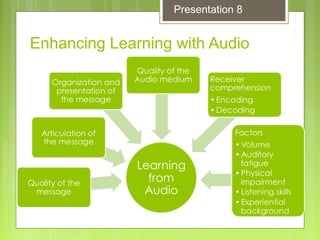
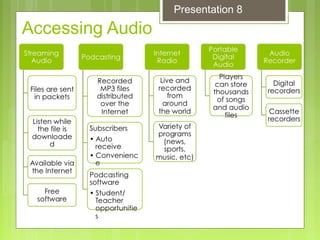
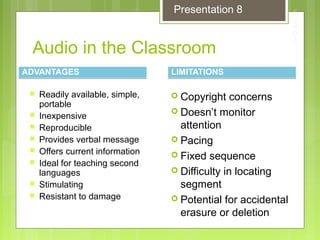
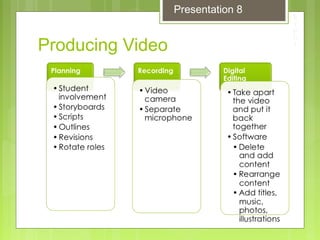
This document discusses enhancing learning with audio and video. It describes the hearing and listening processes and how developing student listening skills can improve learning. It provides information on how teachers and students can use audio resources in the classroom, including prepared recordings, direct instruction, skills practice, interviews, and audio books. Both the advantages and limitations of using audio and video in the classroom are outlined. The document also discusses selecting and producing educational videos, different video formats, and copyright considerations for using audio and video materials.