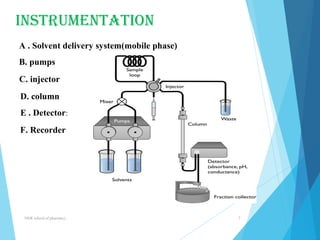
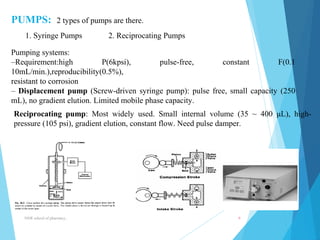
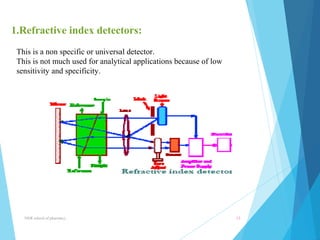
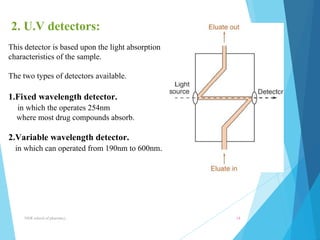
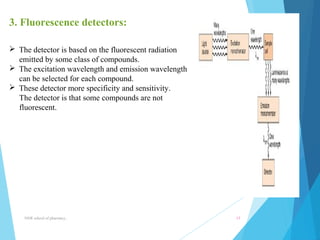
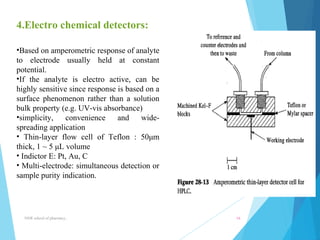
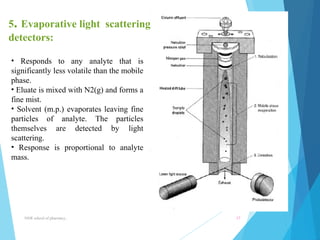
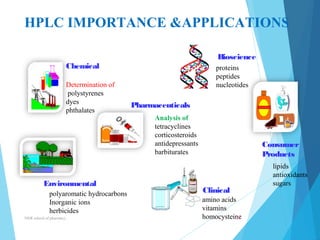
This document provides an overview of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). It defines HPLC as a powerful analytical technique that can separate mixtures of compounds using high pressure to accelerate the mobile phase through the column. The document then describes the basic components of an HPLC system including the solvent delivery system, pumps, injector, column, detectors, and recorder. It also discusses various modes of HPLC separation and provides examples of HPLC applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, biosciences, and environmental analysis.