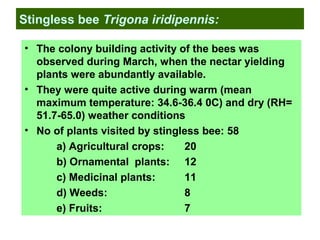
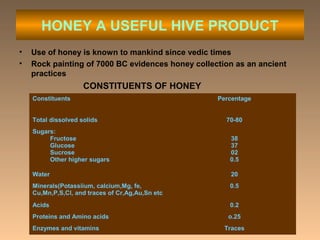
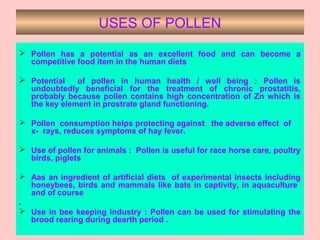
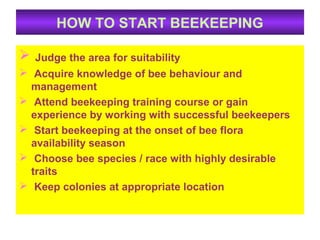
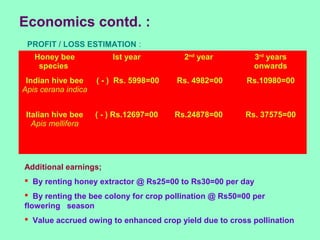
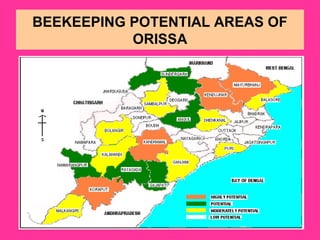
This document provides information on beekeeping and the importance of honey bees as pollinators. It discusses different species of honey bees used for beekeeping in India, as well as hive products like honey, beeswax, bee venom, royal jelly, propolis, and pollen. Honey bees are effective pollinators because their bodies are adapted for pollination through pollen baskets and floral constancy. Their managed populations can significantly increase crop yields and quality through pollination services.