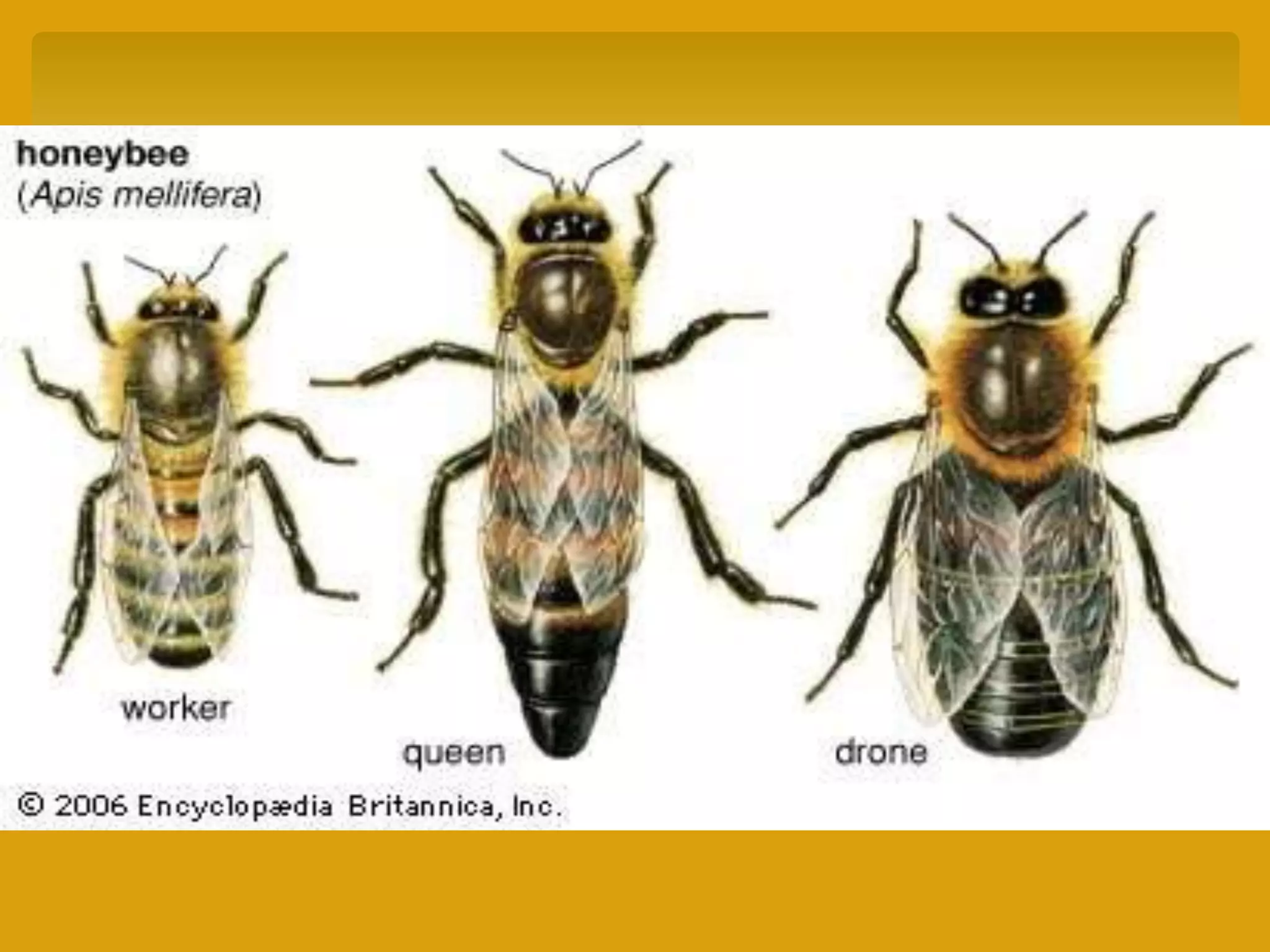
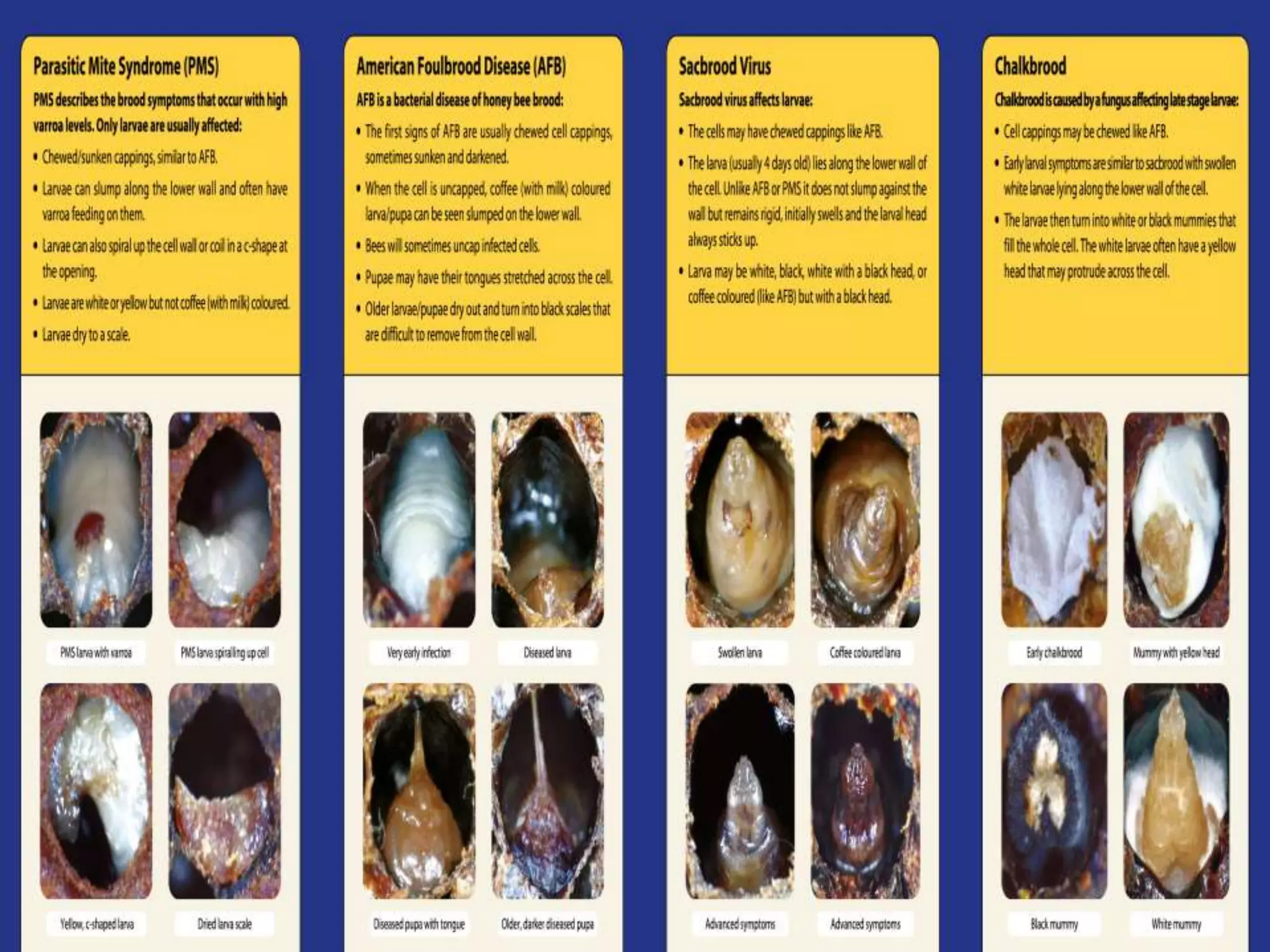
Apiculture is the commercial rearing of honeybees for honey, beeswax, and pollination, gaining popularity in India with significant production and consumption statistics. Various honeybee species, such as Apis dorsata, Apis indica, and Apis mellifera, have distinct characteristics and contributions to honey production and pollination. The document also explains different beekeeping methods, equipment, the composition and preservation of honey, its economic importance, and common bee diseases.