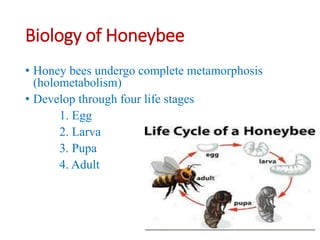
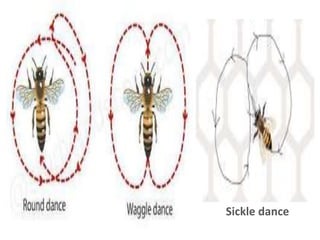
This document summarizes key aspects of bee biology and communication. It describes the four life stages of honeybee development and the three castes in a honeybee colony: queens, workers, and drones. Queens lay eggs and produce pheromones, workers divide labor and duties as they age, and drones mate with queens. The document also explains the three types of honeybee dances - waggle, round, and sickle - used to communicate location and distance of food sources. Finally, it mentions how honeybees use pheromones and food exchanges to share information within the colony.