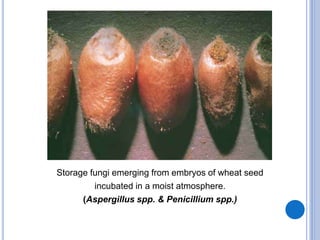
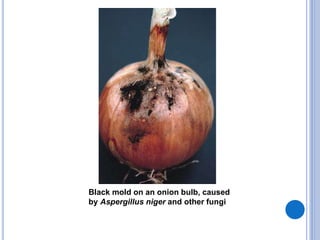
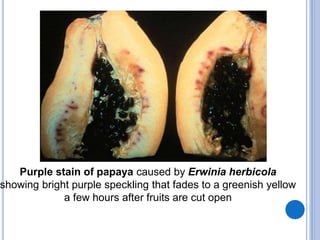
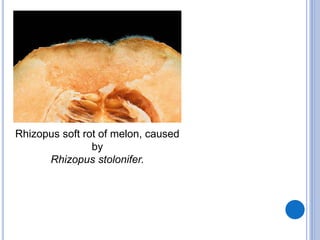
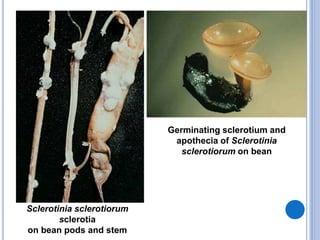
Post-harvest diseases can destroy 10-30% of total crop yields and over 30% in some perishable crops. They develop during harvesting, grading, packing, transportation, storage, and consumption. Major losses occur in fresh fruits and vegetables and grains/legumes. Common post-harvest pathogens include Aspergillus, Penicillium, Erwinia, Monilinia, zygomycetes, and Sclerotinia. They cause diseases such as ear rot, soft rot, purple stain, and white mold. Proper post-harvest handling and storage is important to reduce losses from these diseases.