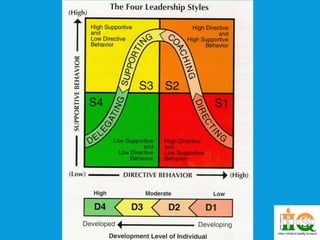
The document discusses various leadership styles including autocratic, bureaucratic, democratic, coercive, transactional, transformational, and laissez-faire. It provides descriptions of each style, when each style is most effective to use, and examples of leaders that embody each style. The document also briefly discusses theories related to leadership such as Theory X and Y and situational leadership theory.