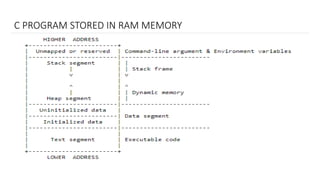
This document explains how a C++ program is stored in RAM, detailing its organization into four segments: text, data, heap, and stack. The text segment contains executable instructions and is read-only, while the data segment holds initialized and uninitialized data. The heap segment is for dynamically allocated memory, and the stack segment stores local variables, managing function calls and local data through stack frames.