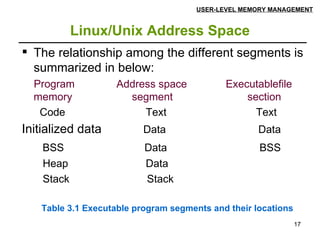
This document discusses user-level memory management in Linux programming. It describes the different memory segments of a Linux process including the code, data, BSS, heap and stack segments. It explains how programs can allocate and free dynamic memory at runtime using library calls like malloc(), calloc(), realloc() and free(), as well as system calls like brk() and sbrk(). Examples of allocating, changing the size, and freeing memory are also provided.




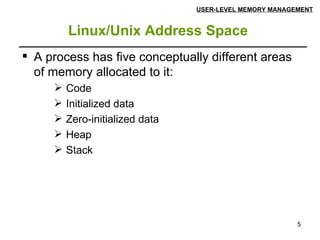



![Linux/Unix Address Space USER-LEVEL MEMORY MANAGEMENT The format of a Linux/Unix executable is such that only variables that are initialized to a nonzero value occupy space in the executable's disk file. Thus, a large array declared 'static char somebuf[2048];', which is automatically zero-filled, does not take up 2 KB worth of disk space. Some compilers have options that let you place zero-initialized data into the data segment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxmemorymanagement-110903102249-phpapp01/85/Linux-memorymanagement-9-320.jpg)