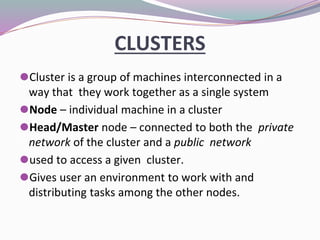
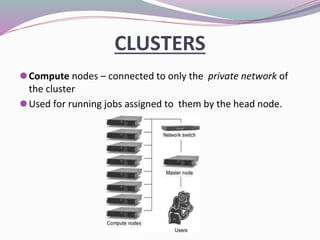
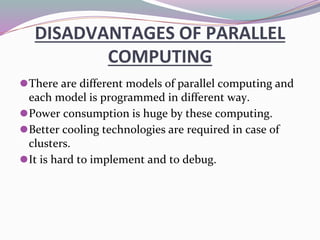
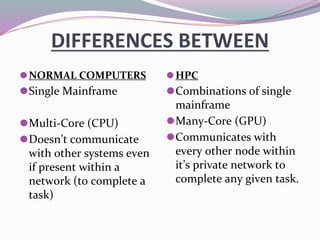
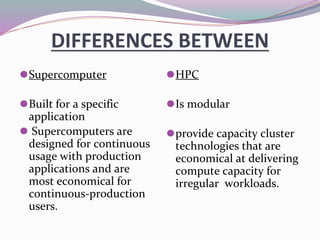
High-performance computers (HPC) aggregate computing power to solve complex problems in various fields such as science, engineering, and business, utilizing parallel processing methods. HPC systems often employ clusters of interconnected machines, improving cost efficiency, processing power, and scalability while offering benefits like enhanced availability and reduced service interruptions. However, HPC is characterized by high costs, significant energy consumption, and challenges in security and transportability.