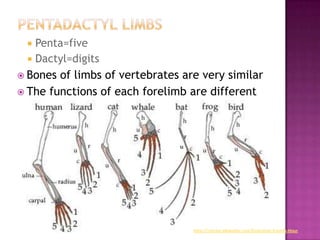
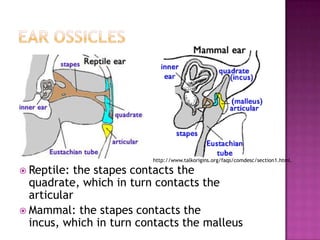
This document defines key terms related to homologous and analogous structures in biology. It explains that homologous structures share an ancestral structure, but may not have the same function, while analogous structures between species have similar functions but different underlying structures. Examples are given of homologous limb bones in vertebrates and vestigial structures providing evidence of evolution from common ancestors. References are also provided.




![ 1. Analogous Structures. Biology Online. [Online] [Cited: September
20, 2010.] http://www.biology-
online.org/dictionary/Analogous_Structures.
2. 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution. Talk Origins. [Online] [Cited:
September 20, 2010.]
http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/comdesc/section1.html.
3. iscid. Homologous Structure. [Online] 2005. [Cited: September
18, 2010.] http://www.iscid.org/encyclopedia/Homologous_Structure.
4. unknown. Evolution. [Online] [Cited: September 18, 2010.]
http://bioweb.cs.earlham.edu/9-12/evolution/HTML/live.html.
5. Allott, Andrew. Evidence for Evolution. Biology. New York : Oxford
University Press, 2007, p. 37.
6. ExamplesOF. Example of Homolgous Structure. [Online] 2010. [Cited:
September 18, 2010.]
http://www.examplesof.com/language/homologous_structure.html.
7. Taylor, Stephen. Evolution. Science Video Recources. [Online] 2010.
[Cited: September 18, 2010.] http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com/bis-
ib-diploma-programme-biology/05-ecology-and-evolution/evolution/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homologousstructure-120314002142-phpapp01/85/Homologous-Structure-Evolution-9-320.jpg)