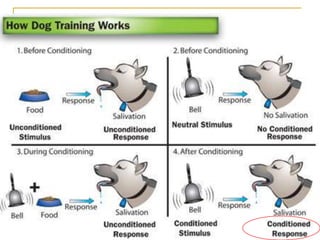
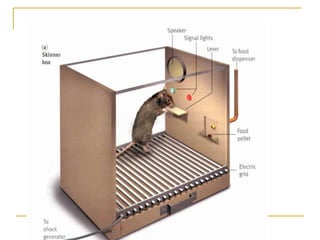
The document discusses animal behavior and its study in ethology. It defines key terms like stimuli, behaviors, and types of learning. Stimuli can be external, like sounds or smells, or internal, like hunger. Behaviors are either innate genetic behaviors important for survival like foraging, parenting or courtship, or learned through processes like imprinting, conditioning, or reasoning. The document categorizes different innate behaviors and provides examples of each, like migration, communication, play, and elimination. It also describes different types of learning animals engage in and provides examples like imprinting, habituation, classical and operant conditioning.