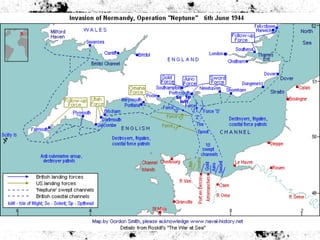
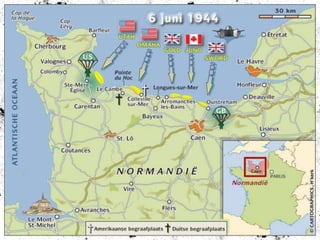
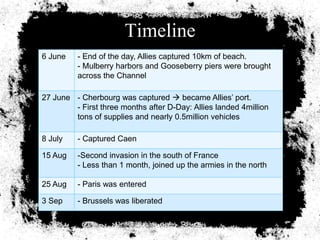
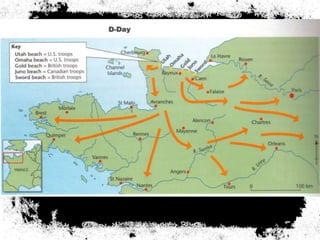
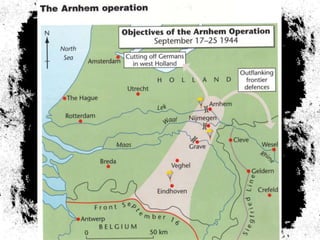
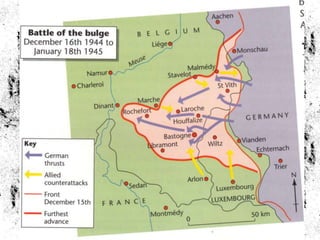
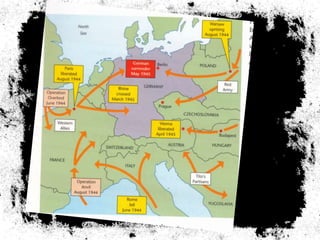
The document summarizes the extensive preparations by the Allied forces for the D-Day landings in Normandy in June 1944. It describes how the Allies chose Normandy as the target location and began training and assembling troops and equipment as early as 1942. Over 7,000 ships were gathered to transport soldiers, weapons, and supplies across the English Channel. Troops underwent special beach landing training, while the Allies worked to conceal the true target location from the Germans. On June 6, 1944, after bombing campaigns softened German defenses, the massive amphibious invasion began across five beaches in Normandy, marking a major turning point in the war.