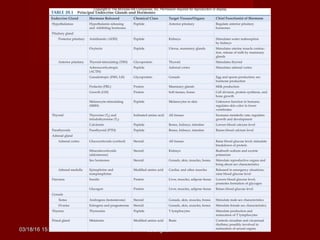
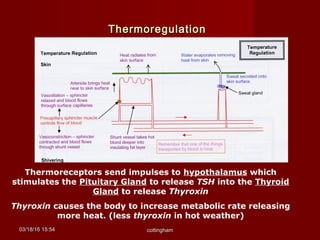
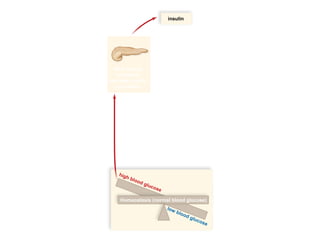
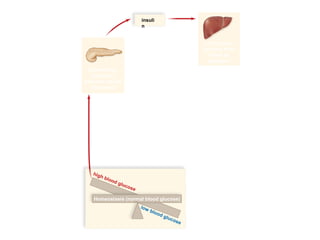
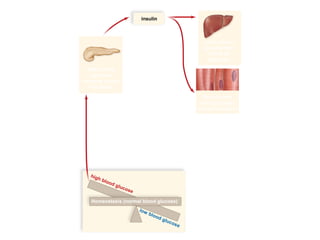
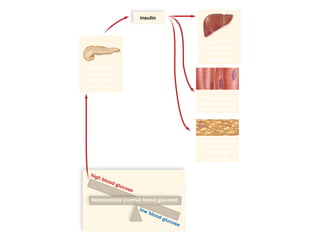
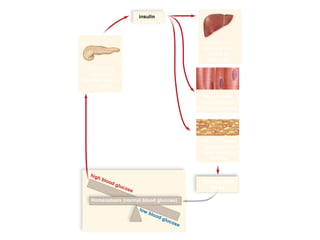
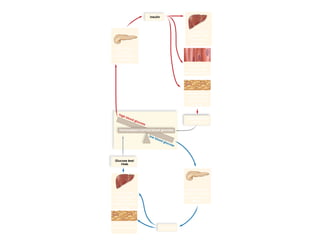
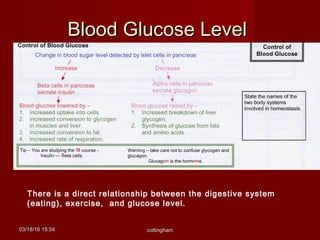
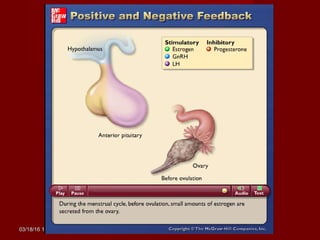
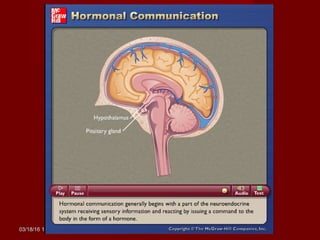
The document discusses homeostasis and various homeostatic mechanisms in the human body. It describes how homeostasis involves negative feedback loops to maintain stable internal conditions. Examples discussed include regulation of body temperature, blood glucose levels, leptin and obesity, and melatonin and sleep patterns. Precise control of these systems relies on coordination between the nervous and endocrine systems, with receptors monitoring variables and effectors enacting changes under brain control.