Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


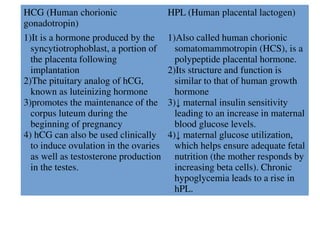
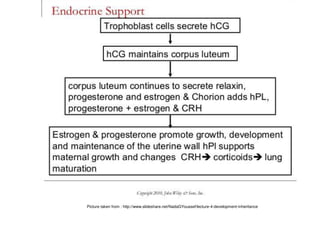
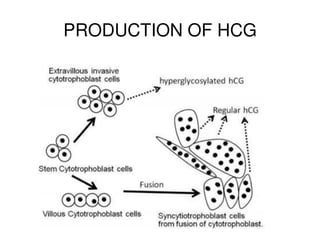

HCG and HPL are protein hormones produced by the placenta. HCG is produced by the syncytiotrophoblast following implantation and promotes maintenance of the corpus luteum during early pregnancy. It can also be used clinically to induce ovulation and testosterone production. HPL, also called HCS, has a similar structure and function to human growth hormone. It decreases maternal insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization to ensure adequate fetal nutrition.





