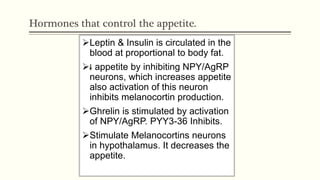
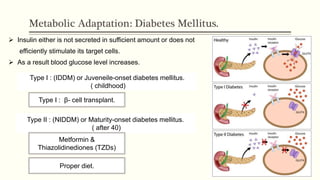
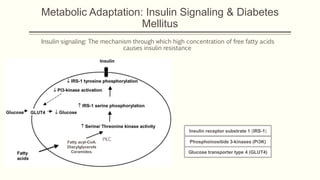
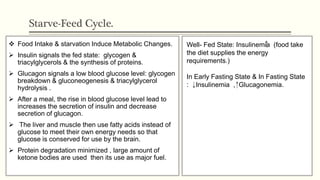
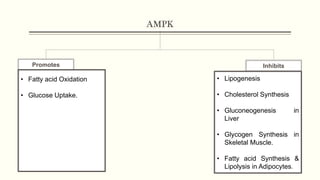
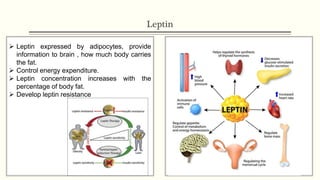
Metabolic homeostasis involves balancing catabolic and anabolic processes to maintain internal stability and allow growth. The AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) regulates metabolic homeostasis by activating catabolism to produce ATP during low energy states and inhibiting anabolism to conserve ATP. Hormones like adiponectin, leptin, and ghrelin also control metabolic homeostasis by regulating AMPK activity and appetite. Disruptions to metabolic homeostasis can lead to diseases like diabetes mellitus.

![AMP-dependent protein kinase(AMPK).
Regulate Metabolic Homeostasis.
Activates Catabolism ATP.
Inhibits Anabolism to conserved ATP.
It targets include the heart isozyme of the bifunctional enzyme PFK-2/FBPase-2 which control
(F2,6P) concentration.
Ischemic Diseases (deficient supply of blood to a body part)
Oxygen Oxidative Phosphorylation [Concentration of ATP.]
AMP buildup Anaerobic Glycolysis [ ATP production.]
SWITCH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolichomeostasis-210701112357/85/Metabolic-homeostasis-3-320.jpg)
![Adiponectin
It regulates AMPK activity.
247- residue protein hormone, secreted by adipocytes.
[ Energy homeostasis, Glucose & Lipid metabolism by controlling AMPK activity]
The binding of adiponectin to it’s receptors i.e. on the surface of liver & muscle cells. Increases
phosphorylation & activity of AMPK.
It Inhibits: Gluconeogenesis
Stimulates: Fatty acid oxidation in liver, Glucose uptake. Also in Muscles.
Increases Insulin sensitivity.
Hormone decreases lead to various diseases. (Type 2 Diabetes)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolichomeostasis-210701112357/85/Metabolic-homeostasis-5-320.jpg)

![Control of energy expenditure by Adaptive
Thermogenesis.
The energy is utilized by an
organisms either by
performance of work or the
generation of heat.
The other diet-induced
thermogenesis & form of
adaptive thermogenesis.
Norepinephrine
Release
Binds
Adernergic receptor
on brown fat
Increases cAMP,
enzymatic phosphorylation
Activates
Hormone sensitive Triacylglycerol
lipase
Increases free fatty acid
fuel
Oxidation.
Opening of protein
channel [UCP1] or
Thermogenin
ATP production
Heat
Mechanism of Thermogenesis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolichomeostasis-210701112357/85/Metabolic-homeostasis-8-320.jpg)