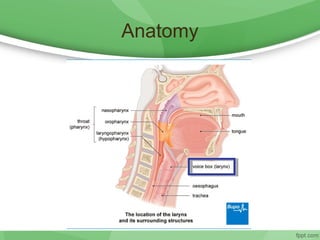
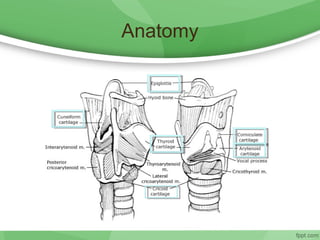
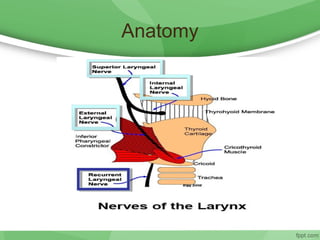
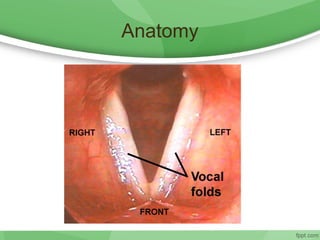
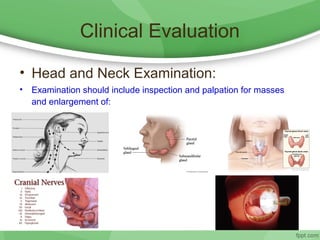
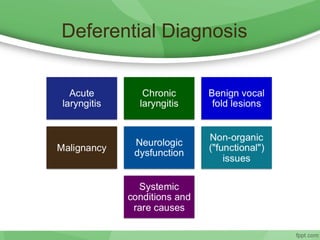
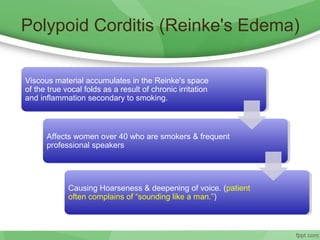
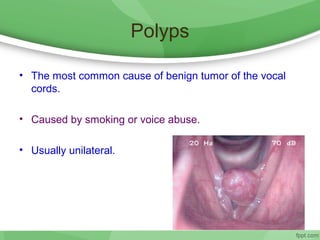
This document discusses hoarseness, including its definition, anatomy, etiology, clinical evaluation, differential diagnosis, and management. Hoarseness refers to any change in voice quality and can be caused by infections, polyps, smoking, acid reflux, and other factors. The clinical evaluation of hoarseness involves taking a medical history, performing a physical exam including laryngoscopy, and considering differential diagnoses such as laryngitis, vocal fold lesions, laryngeal carcinoma, and neurologic dysfunction. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include voice rest, voice therapy, pharmacotherapy, and surgery.