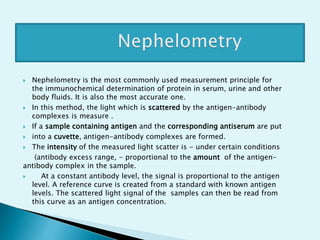
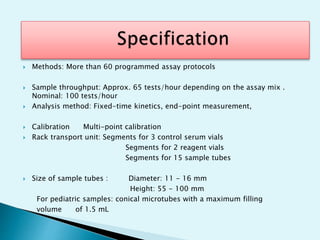
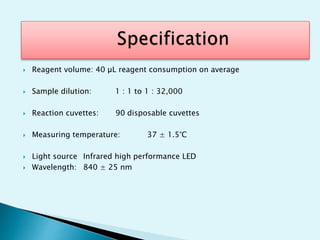
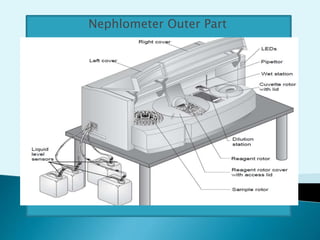
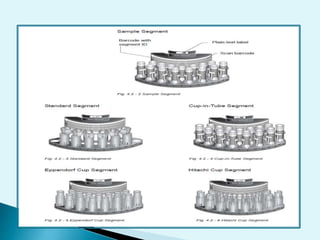
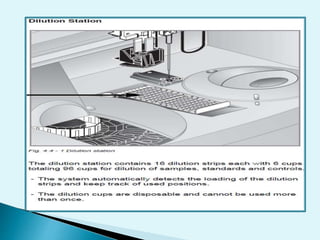
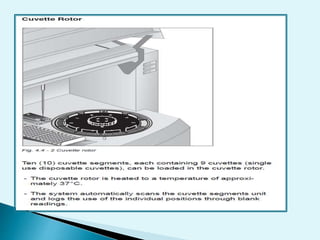
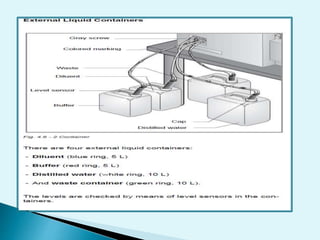
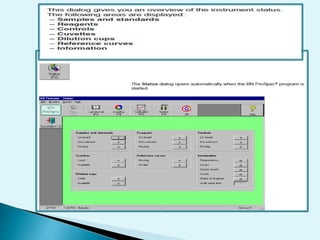
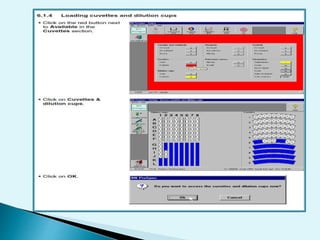
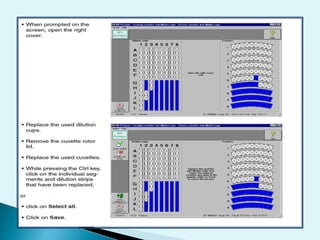
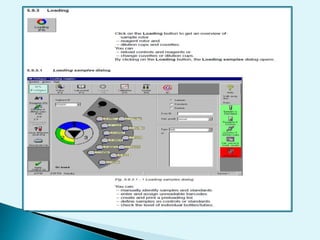
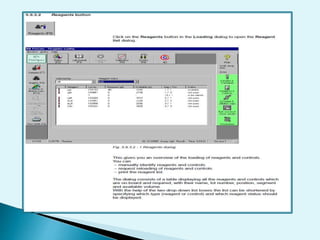
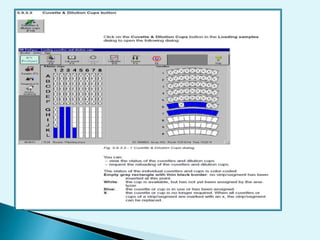
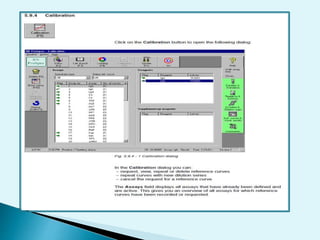
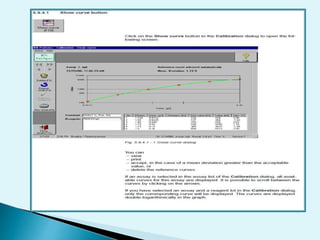
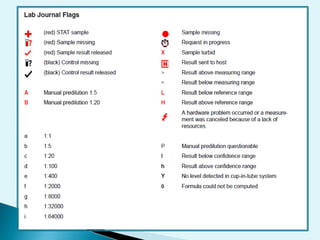
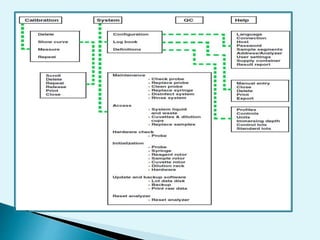
Nephelometry is commonly used to determine protein levels in body fluids like serum and urine. It works by measuring the light scattered by antigen-antibody complexes formed when a sample containing antigen is mixed with corresponding antiserum. The amount of light scattered is proportional to the antigen concentration in the sample. This document provides instructions for using a nephelometer to test samples for C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, including preparing reagents and standards, running samples, generating a calibration curve from standards, and recording results. CRP levels between 0.0-1.0 mg/dL are considered normal.