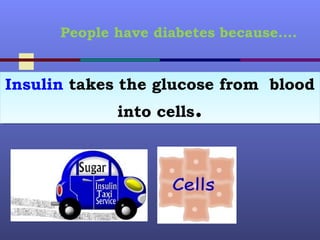
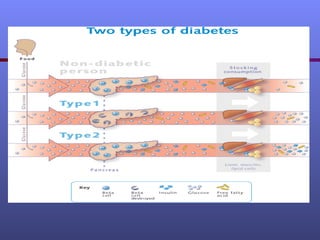
Diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or the cells ignore the insulin. There are two main types of diabetes - type 1 where the body does not produce insulin and type 2 where the body does not produce enough insulin or cells ignore it. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications affecting eyes, kidneys, heart, nerves, and feet. Management involves monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and potentially taking medications or insulin injections. The goal is to control blood sugar and prevent or delay complications through an optimal treatment plan.