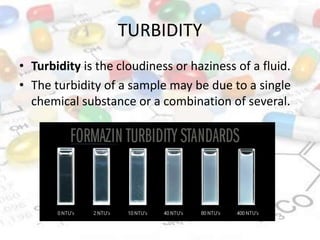
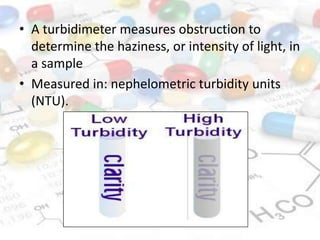
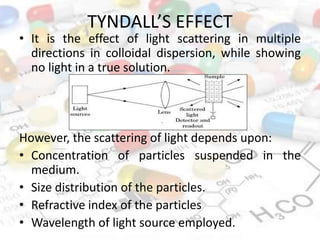
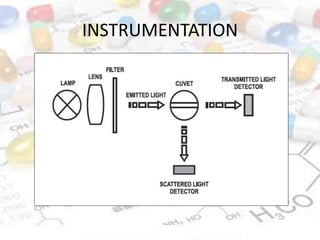
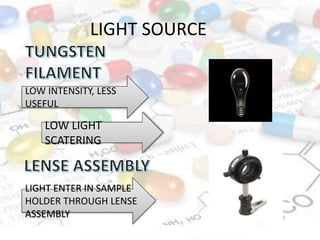
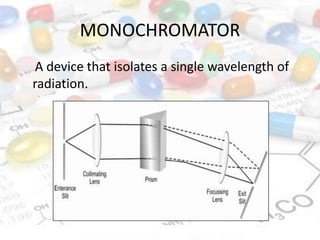
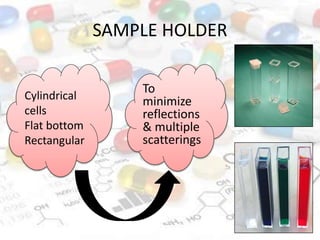
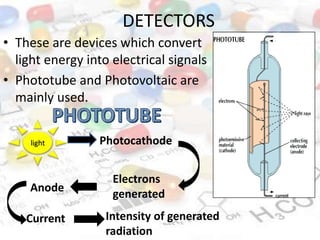
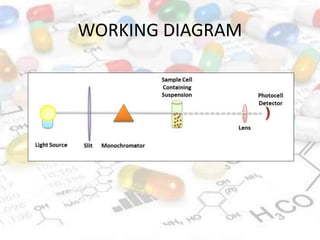
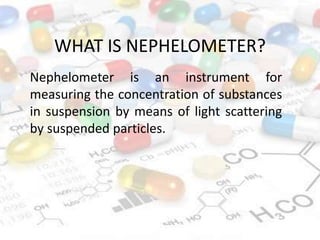
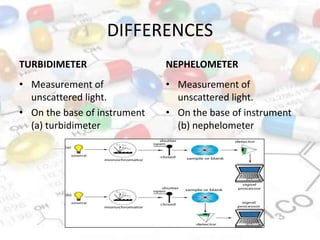
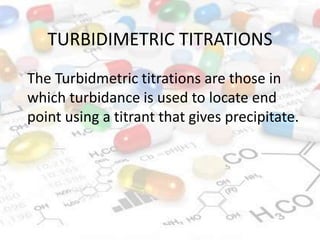
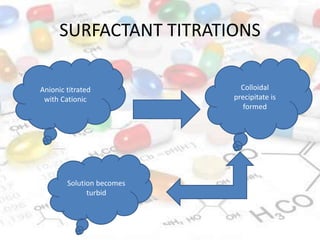
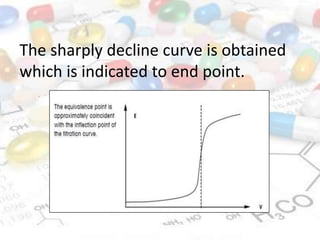
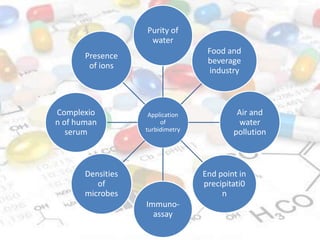
This document discusses turbidimetry and nephelometry. Turbidimetry measures cloudiness or haziness in a fluid sample by detecting scattered light, while nephelometry specifically measures light scattering. Both operate on the principles of light absorption and scattering when passed through a sample. A turbidimeter/nephelometer contains a light source, sample holder, and detector and can be used to measure water and air pollution, detect contaminants, and determine endpoints in titrations. Turbidimetry has applications in water treatment plants and the food industry and provides advantages of low cost and not requiring zero adjustments, though it cannot determine particle size and bubbles can interfere with readings.