C-reactive protein (CRP) is a liver-produced protein that indicates inflammation and is measured by a CRP test to assess acute conditions or monitor chronic diseases. The high sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) test is used for seemingly healthy individuals to evaluate heart disease risk, while the regular CRP test is intended for those with potential infections or inflammatory diseases. The document outlines the procedure for conducting a CRP test, including preparation, controls, and interpretation of results.



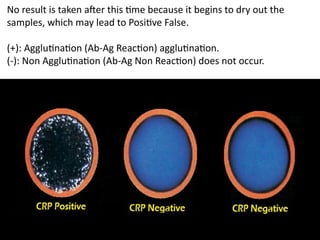
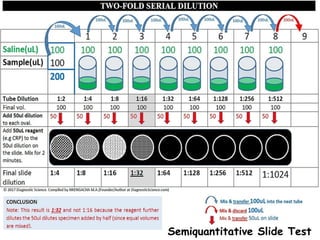
![Topic : Immunological Test [ C-Reactive Protein (CRP) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-reactiveproteincrp-241219194015-58e6b7e6/85/Topic-Immunological-Test-C-Reactive-Protein-CRP-6-320.jpg)