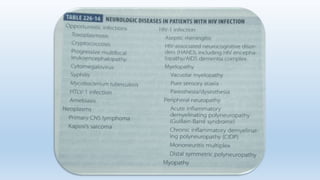
This document summarizes several neurological conditions associated with HIV, including:
1. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND), which has three stages from asymptomatic to HIV-associated dementia.
2. Aseptic meningitis, cryptococcal meningitis, toxoplasmosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), and spinal cord diseases like vacuolar myelopathy are also discussed.
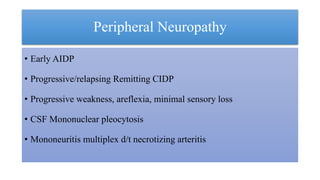
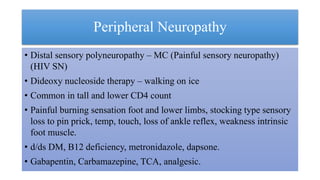
3. Peripheral neuropathies are common, especially a painful sensory neuropathy, as well as myopathies related to HIV or antiretroviral medications.