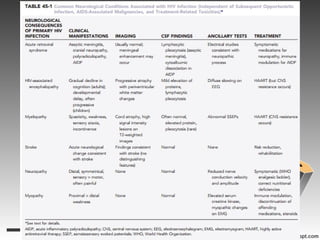
This document summarizes various neurological complications of HIV/AIDS, including:
- Acute retroviral syndrome occurring in the majority after initial HIV exposure, potentially causing meningitis.
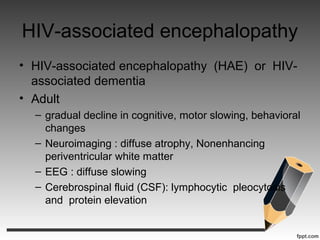
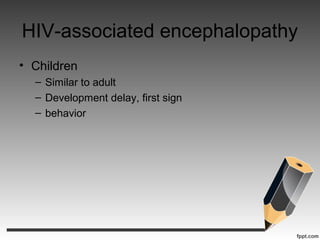
- HIV-associated encephalopathy, the most common HIV-related brain disease, presenting as cognitive and motor slowing.
- Myelopathy, characterized by vacuolar changes in the thoracic spinal cord causing spasticity and sensory symptoms.
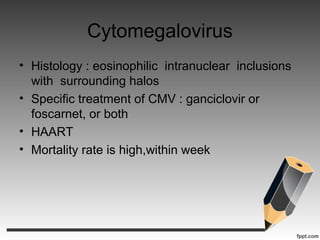
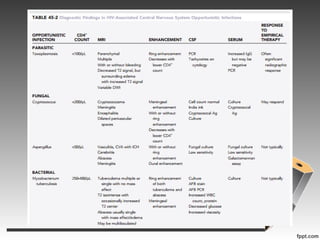
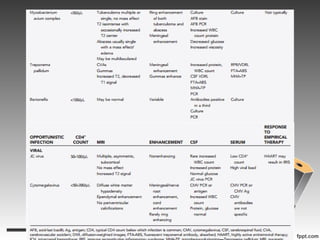
- Several types of infections are described like toxoplasmosis, cryptococcus, CMV, and various types of mycobacteria.
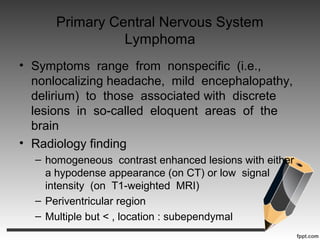
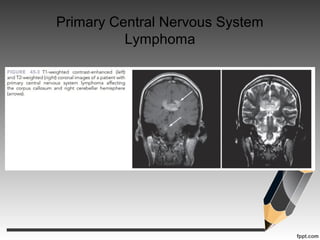
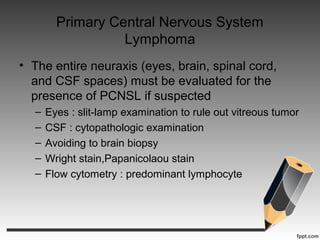
- Primary central nervous system lymphoma is an AIDS-defining cancer that can involve the brain, eyes and spinal fluid.
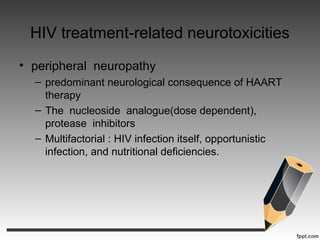
- Neurotoxic