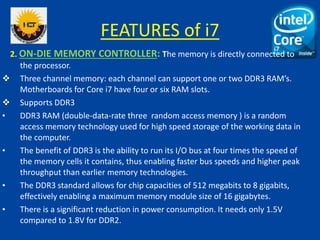
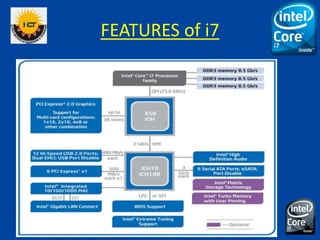
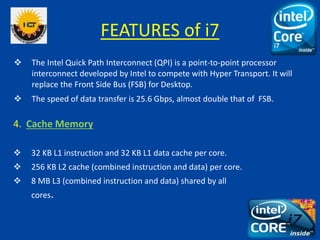
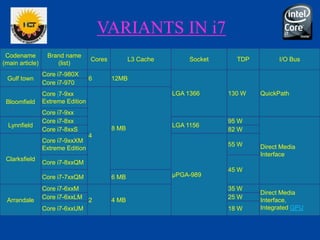
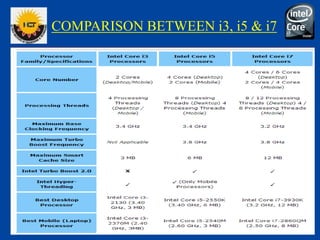
The document is a comprehensive presentation on the Intel Core i7 processor, detailing its architecture, features, and variations compared to other Intel Core processors. It explains the benefits of the i7, such as increased speed, large cache size, and advanced technologies like hyper-threading and turbo boost, while also noting its disadvantages, including high cost and power consumption. The conclusion highlights the i7's superior performance over previous models and anticipates the future release of the i9 version.