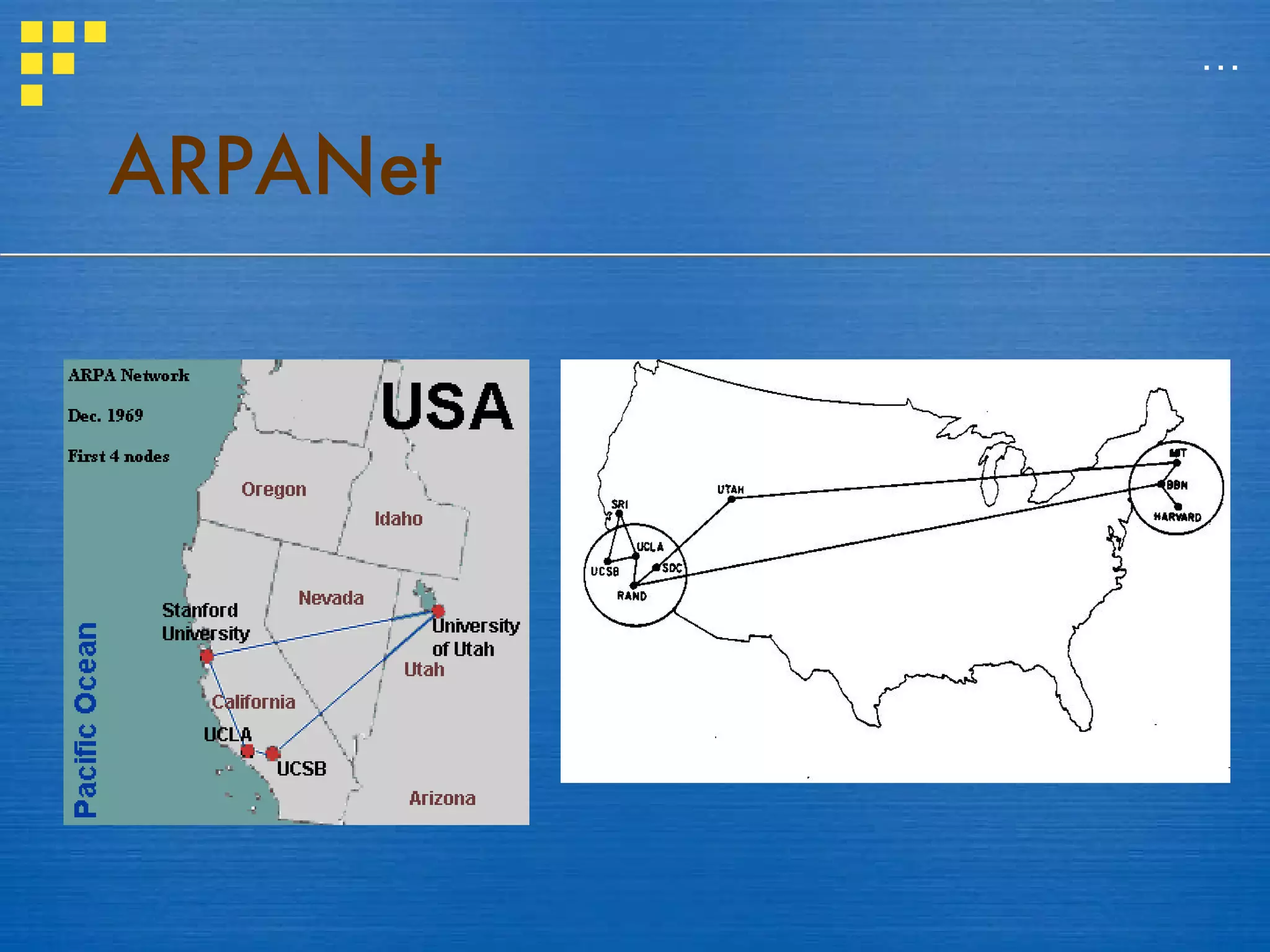
The document provides a history of the internet and world wide web, beginning with the creation of ARPANET by the US Department of Defense and MIT in response to the launch of Sputnik. It then discusses the development of early internet protocols in the 1970s and the creation of the world wide web by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in the 1980s. Finally, it outlines how the internet functions today using protocols like TCP/IP and HTML to transmit and display data through web browsers.















![Internet Addresses (aka Canonical Addresses) are associated with the IP Address Registered at the same time Also called DNS (Domain Name System) [email_address] (e.g.: smccombs@uh.edu) Connecting to the Internet /cont./](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoftheinternet-110118175356-phpapp01/75/History-Basic-Structure-of-the-Internet-20-2048.jpg)





