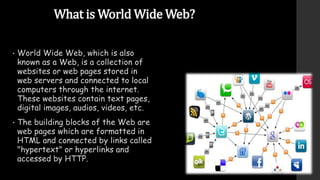
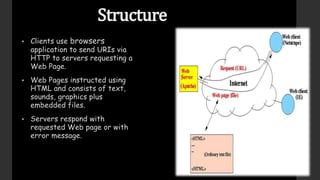
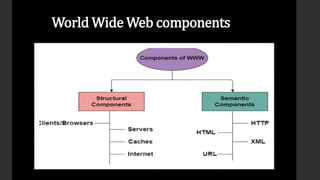
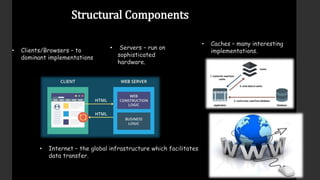
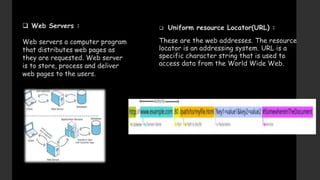
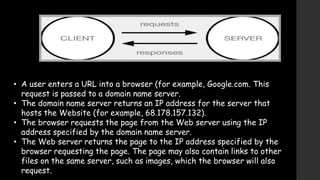
The document provides an overview of the history and components of the World Wide Web (WWW). It discusses how Tim Berners-Lee invented the WWW in 1989 while working at CERN to help scientists share research online. The core components that make up the WWW include clients/browsers, servers, hypertext transfer protocol, hypertext markup language, and uniform resource identifiers. The document also distinguishes the WWW from the underlying Internet and describes how the WWW works using these components.