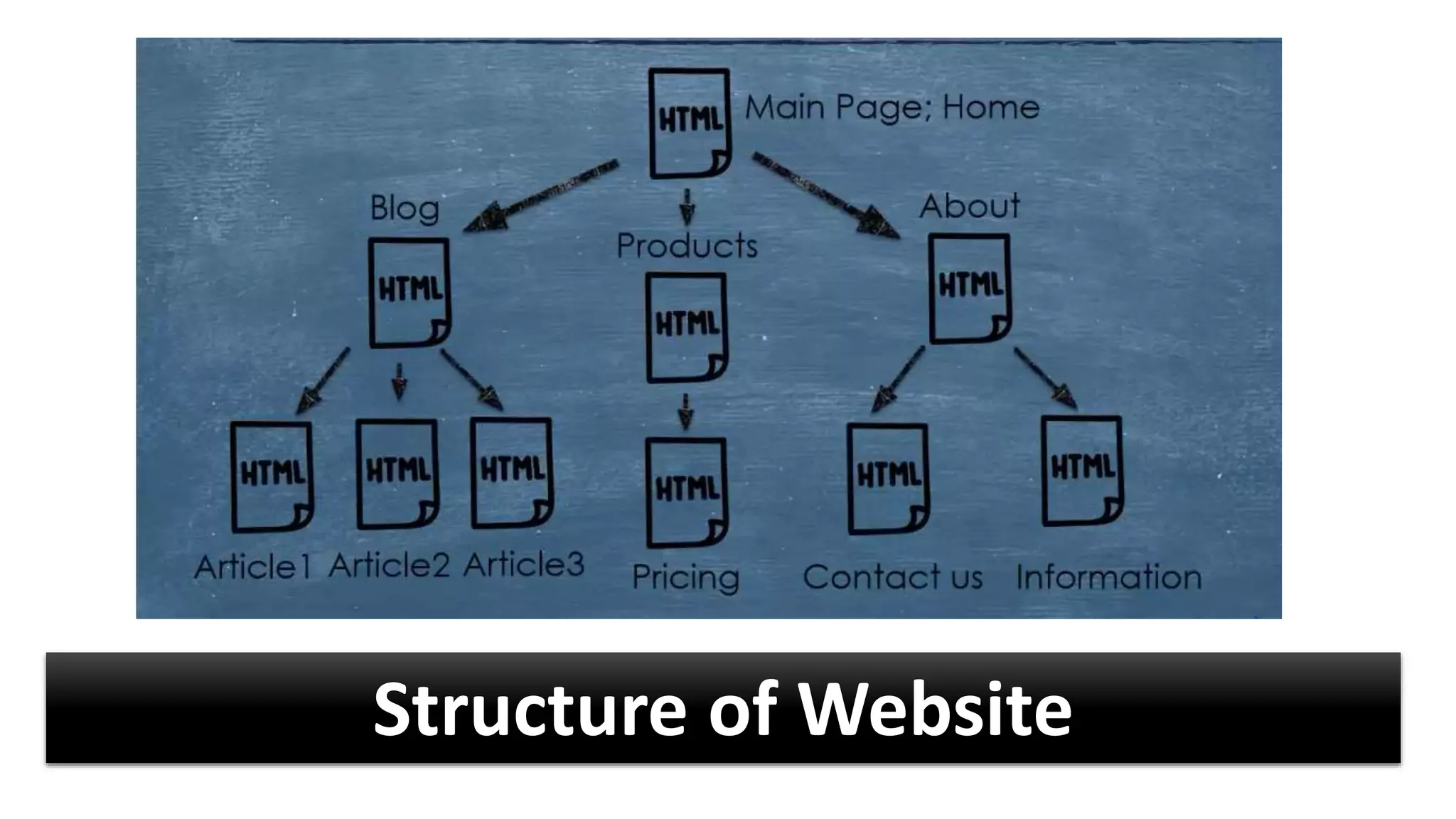
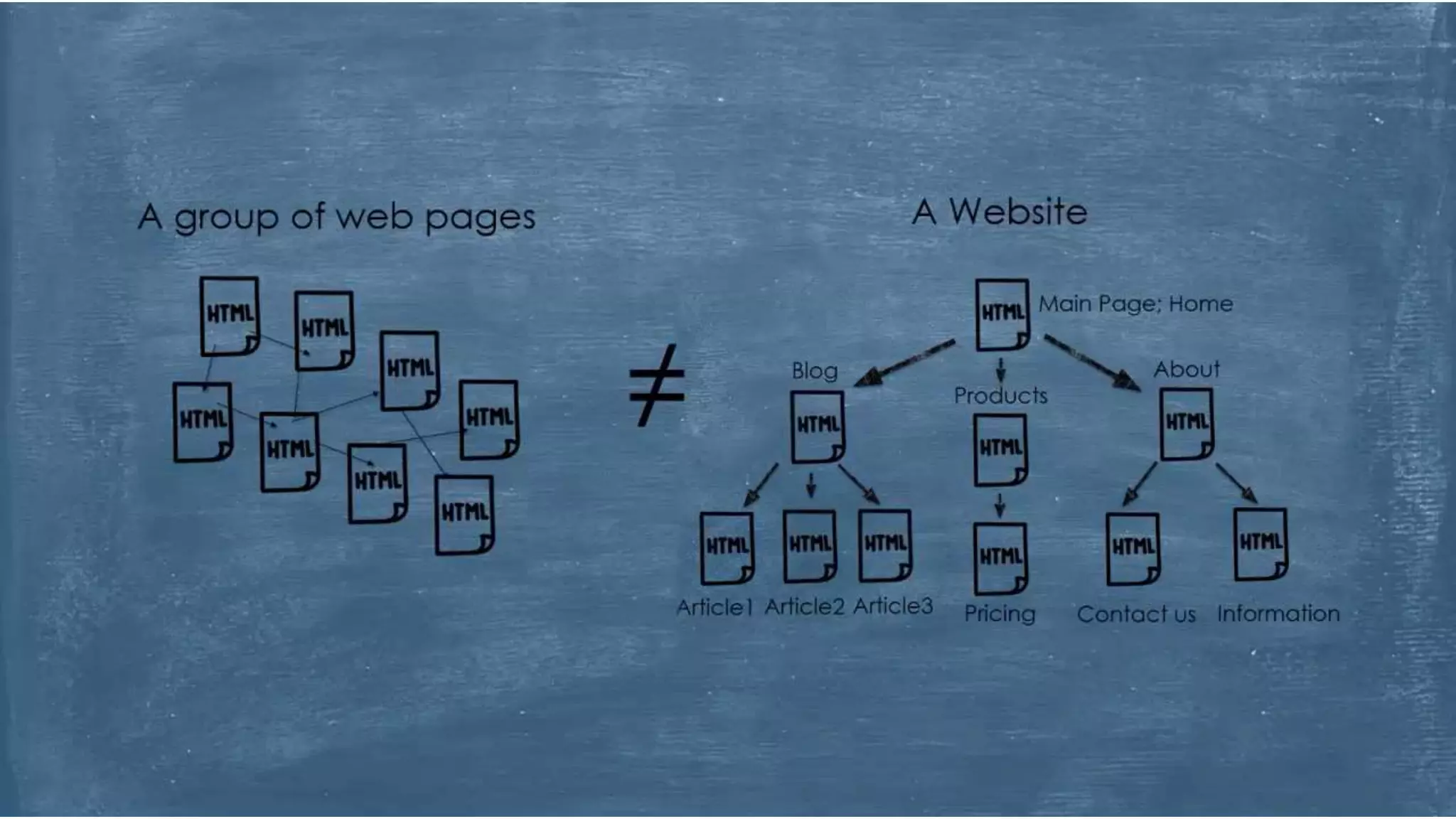
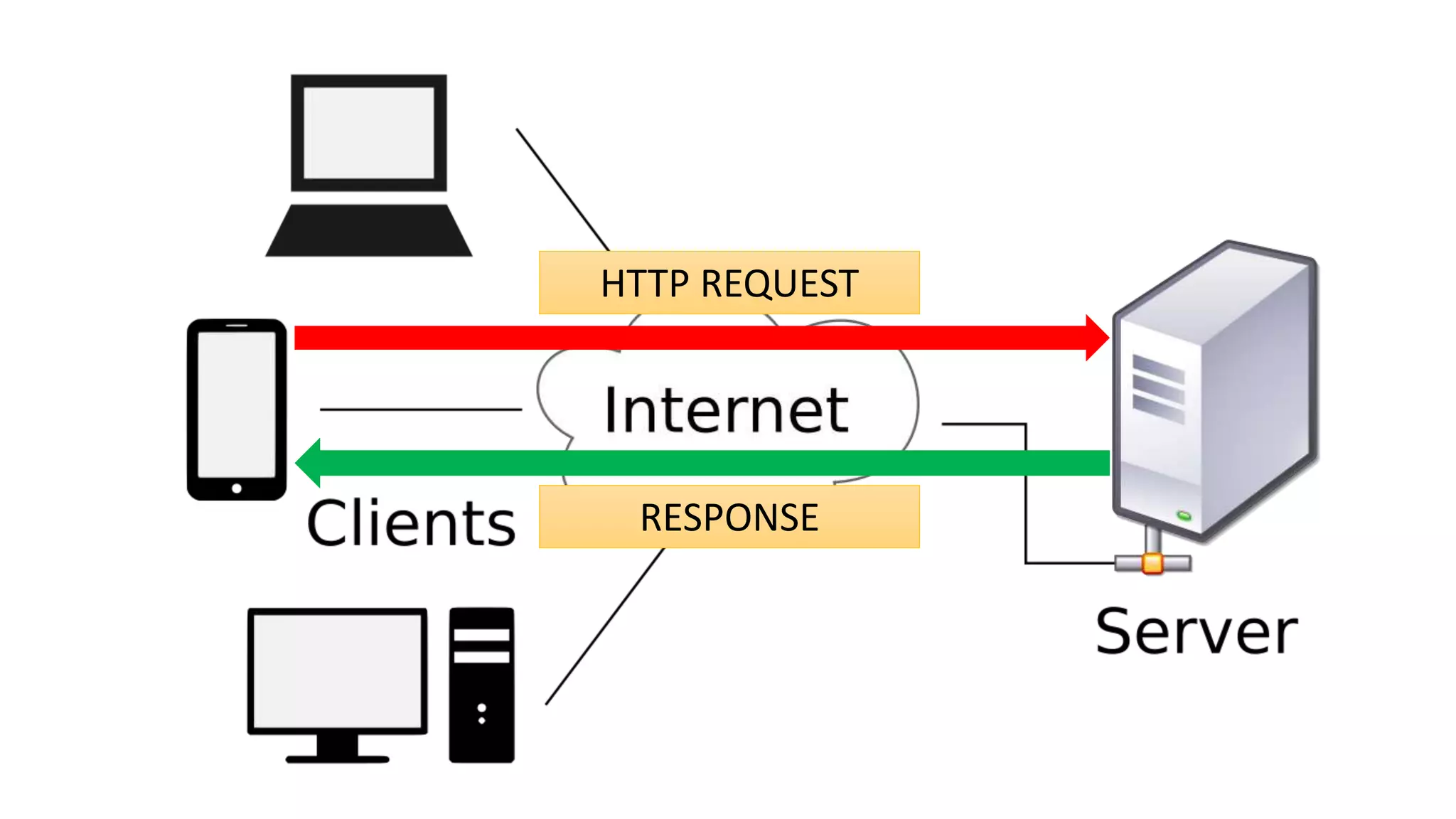
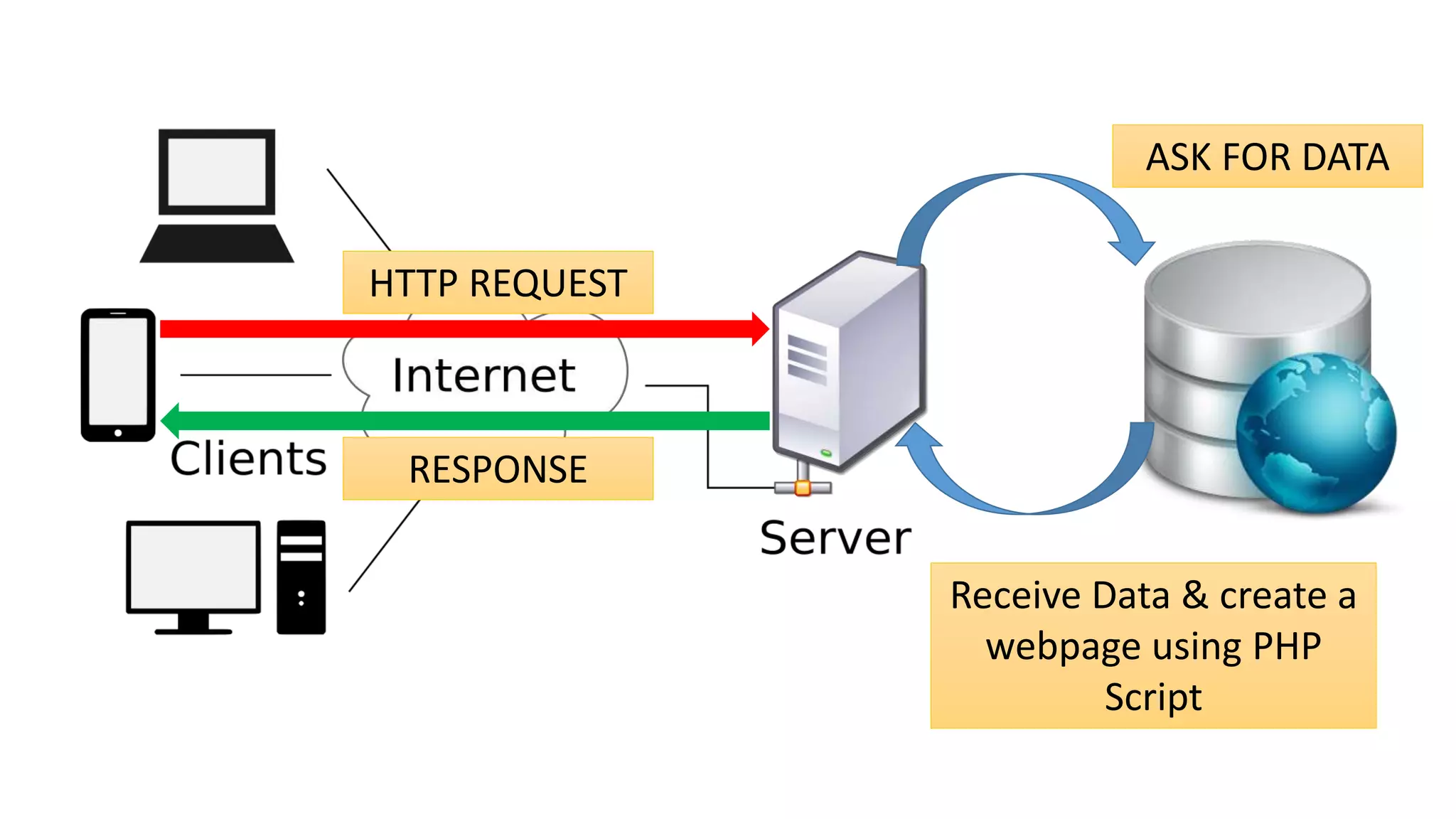
The World Wide Web was created in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee as a way to share scientific documents over the Internet. It uses HTML pages that can be accessed via HTTP and linked together through hyperlinks. While often used interchangeably, the Web is actually a subset of the larger Internet, which includes other applications like email and file transfer. The Web evolved from static publishing in its early Web 1.0 stage to include more participation and social features in Web 2.0, and aims to add semantic capabilities in its ongoing development of Web 3.0.